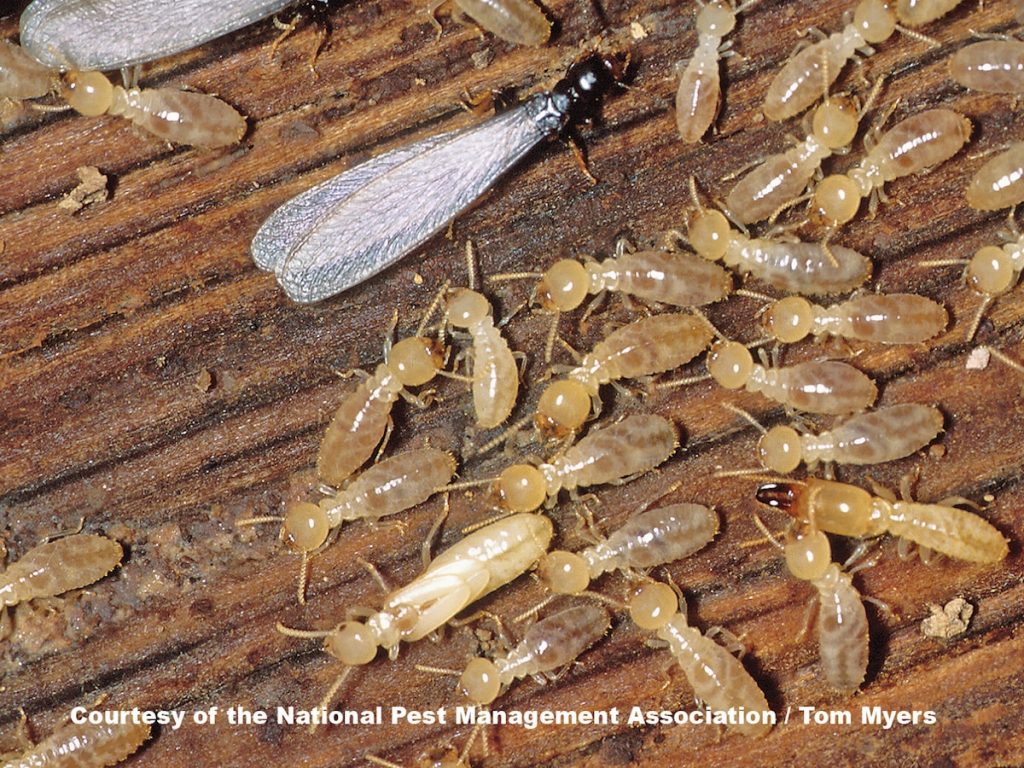
Termites are small, wood-eating insects that cause significant damage to wooden structures and furniture. They are typically found in the southern United States, but can also be found in other parts of the world. The origin of termites is still a matter of debate among entomologists, but it is believed that they have existed since the Cretaceous period, some 145 million years ago. Termites are believed to have evolved from a species of cockroach, and they are closely related to ants and bees. In this article, we will discuss the origins of termites, and explore the different theories of where they come from.
Types of Termites
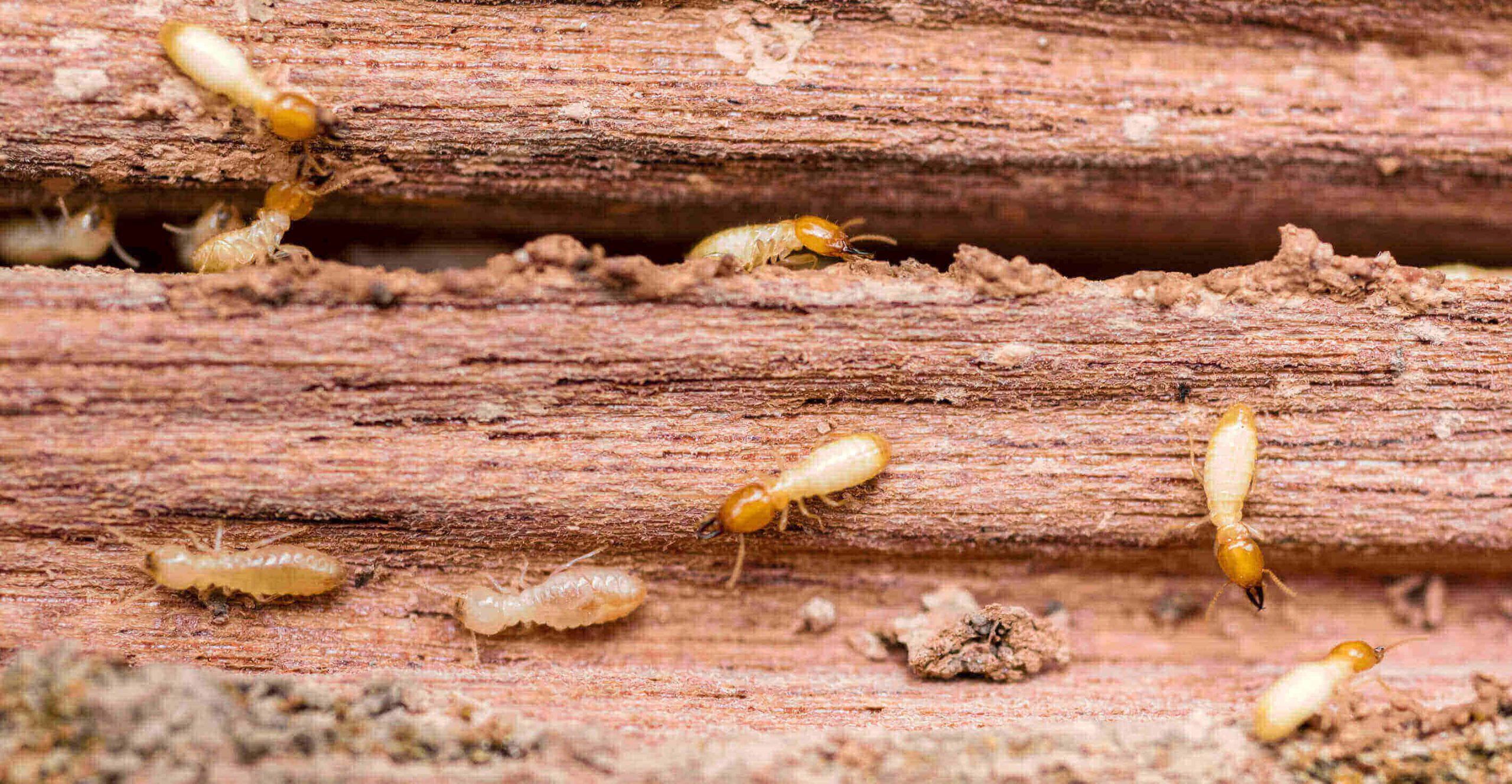

Subterranean Termites
Subterranean termites are the most common type of termite found in the United States and are found in all states except Alaska. They build their colonies underground and enter homes through cracks in the foundation or other openings.
Formosan Termites
Formosan termites are an invasive species that have been found in the southeastern United States. They are known to build large colonies with extensive underground tunnel systems. They can cause extensive damage to homes if left untreated.
Drywood Termites
Drywood termites are found in the southern and western United States. They are known to infest wood that is already in a home, such as furniture, wood beams, and other wood products.
Dampwood Termites
Dampwood termites are found in the western United States and prefer wood that has been previously wetted by water. They can cause significant damage to homes if left untreated.
Natural Habitats of Termites

Subterranean Termites
Subterranean termites live in colonies underground and build tunnels to access food sources above ground. These tunnels are made of soil and saliva, and are known as “mud tubes”. Subterranean termites are found throughout the US, and prefer warm, moist climates. They can survive in a variety of environments, including forests, grasslands, agricultural areas, and urban settings.
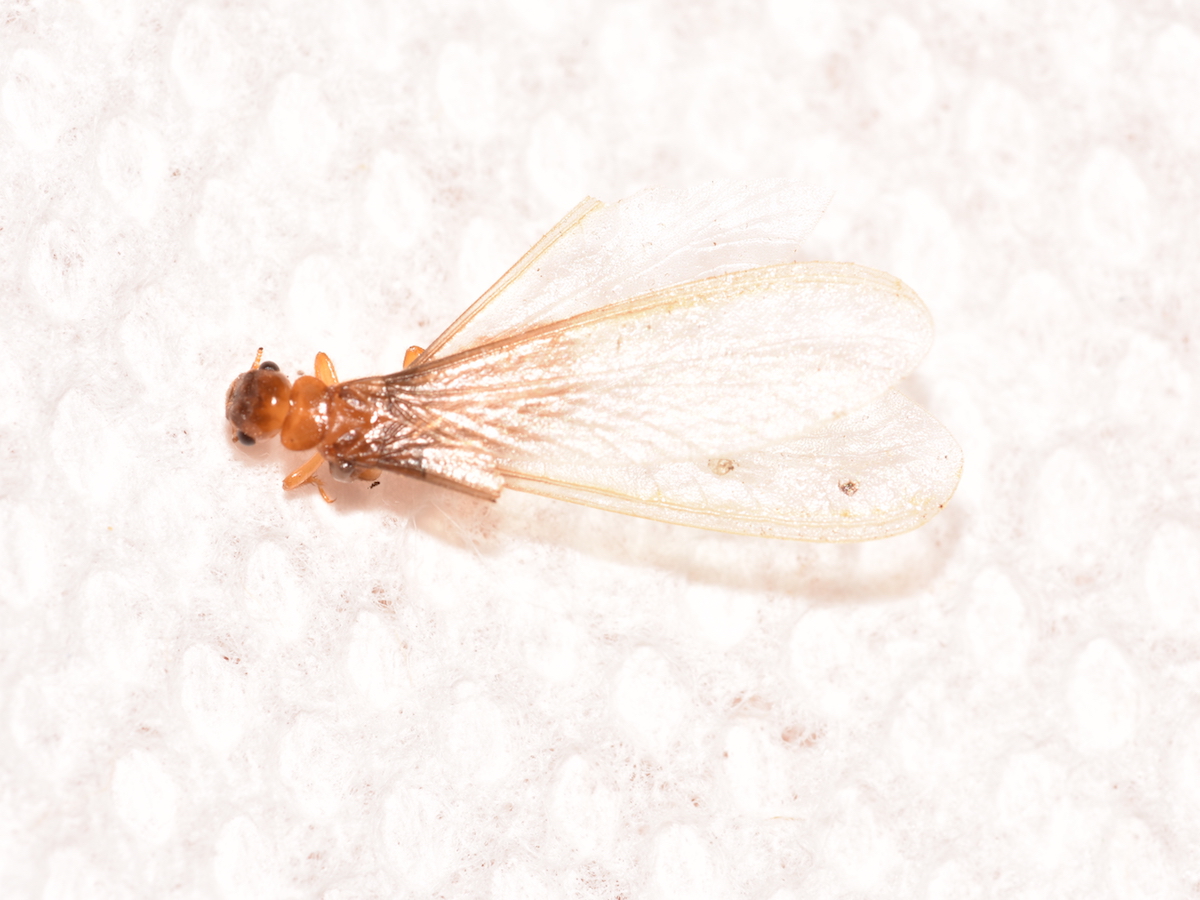
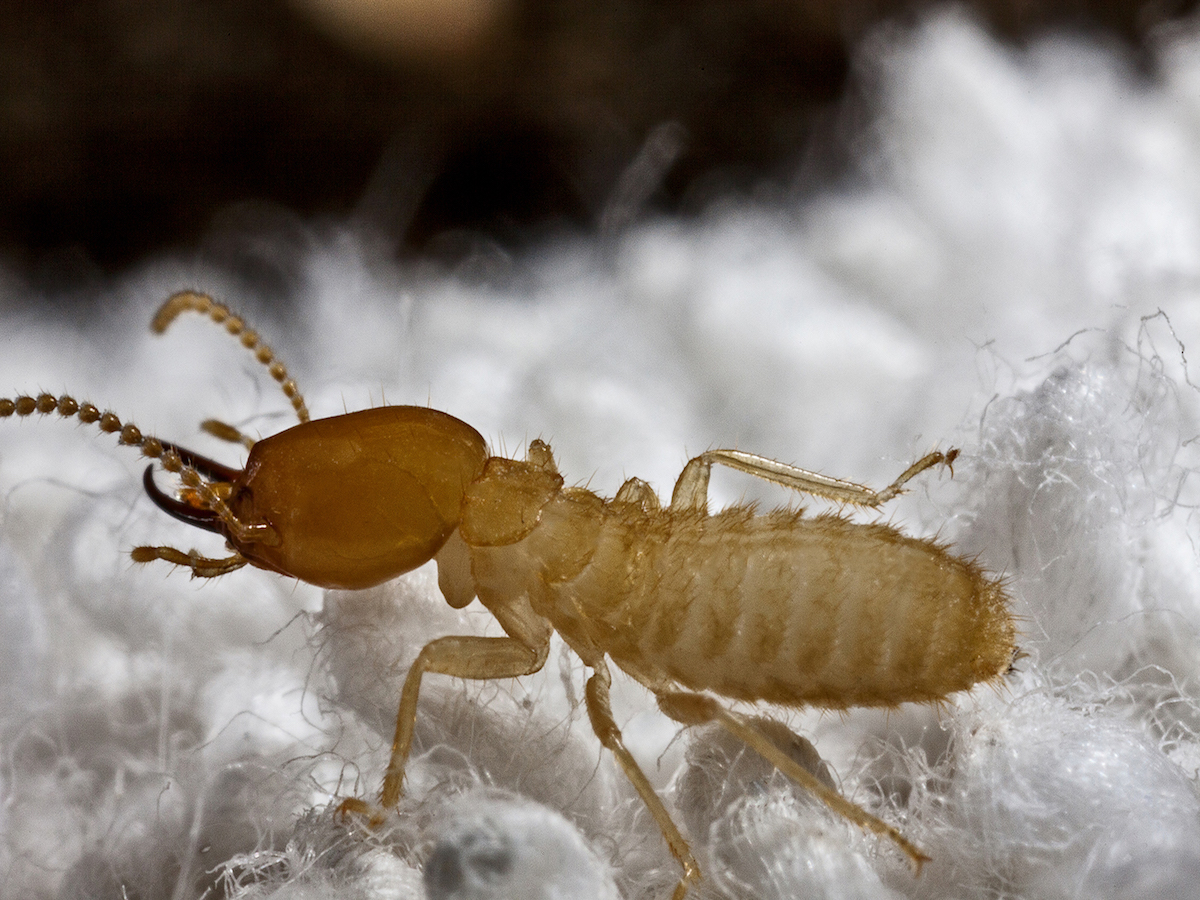
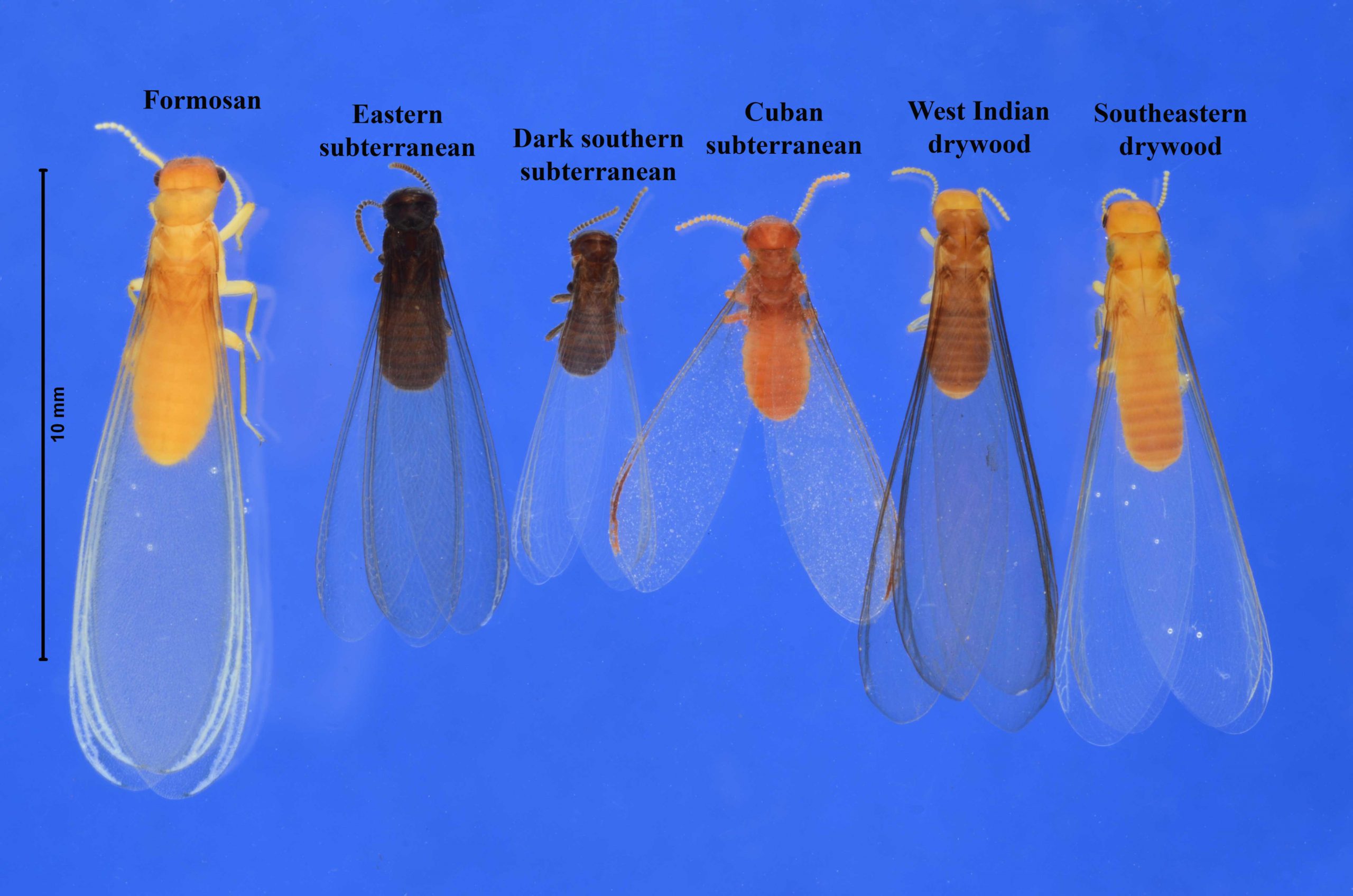
2 Formosan Termites
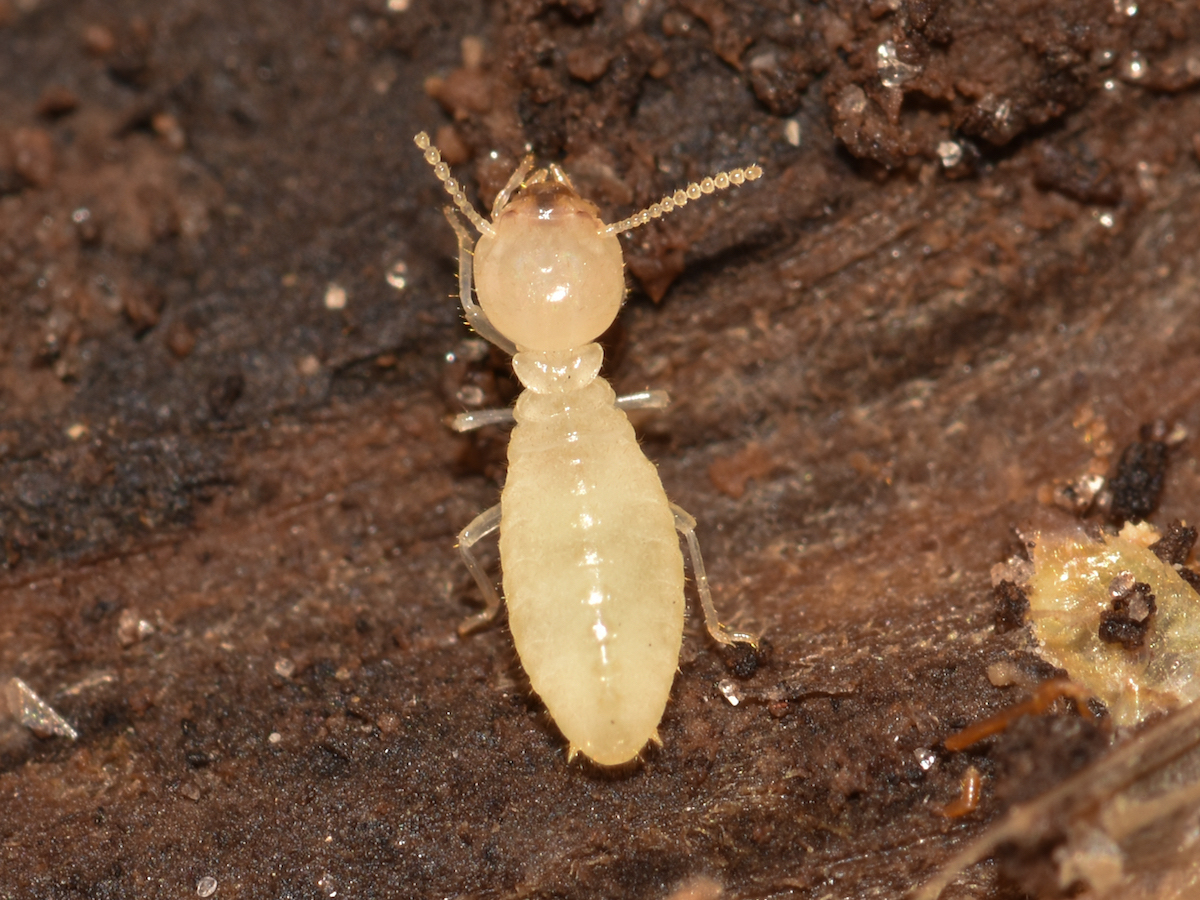




| Scientific Name | Origin |
|---|---|
| Coptotermes formosanus | South Asia and Southern China |
| Reticulitermes flavipes | South Asia and Southern China |
Formosan termites are two closely related species of subterranean termite, Coptotermes formosanus and Reticulitermes flavipes. Both species have a wide distribution and are found from South Asia to Southern China. They are known for their destructive behavior and have caused extensive damage to buildings throughout their range.
3 Drywood Termites
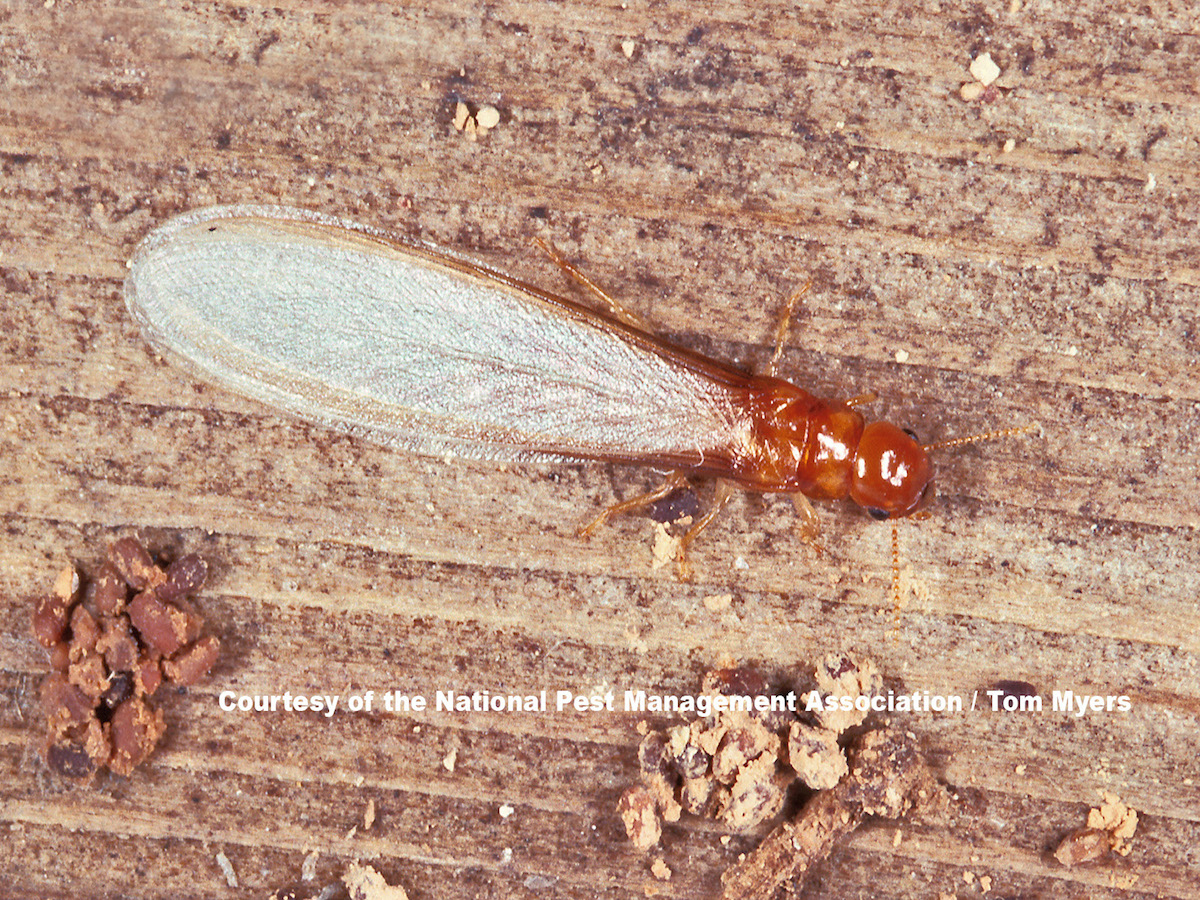
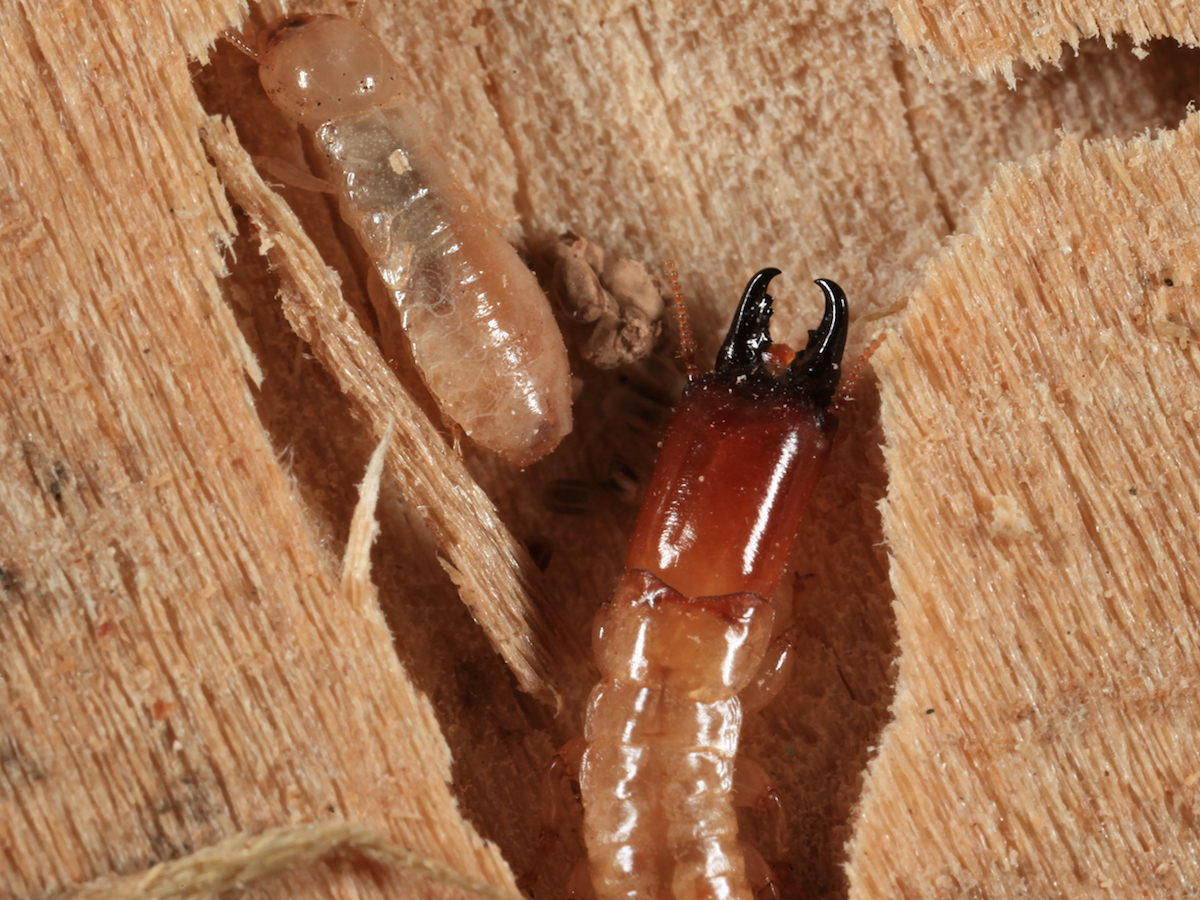



Drywood termites are found in many parts of the world, including the southern United States, Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, and tropical regions of South America. These termites live in dry wood, such as structural wood in homes and furniture. They can enter a structure through cracks in walls or roofs, or through exposed wood surfaces. Drywood termites typically establish smaller colonies than subterranean termites, but they can still cause extensive damage to structures.
Drywood termites feed on cellulose-based materials, including wood, paper, and other plant-based materials. They create tunnels through the wood and leave behind a powdery material called frass, which is a combination of feces and undigested wood particles. Drywood termites also leave behind fecal pellets that are about 1/32 of an inch in length. These pellets are a telltale sign of a drywood termite infestation.
Drywood termites can be difficult to control because they do not need contact with the soil like subterranean termites do. They can survive in a structure for long periods of time without being detected. To control drywood termites, homeowners should use chemical treatments and baiting systems to monitor activity and prevent infestations. Professional pest control services may also be necessary to eliminate an established drywood termite colony.
4 Dampwood Termites
Dampwood termites are found throughout the world and are common in damp and decaying wood, both in homes and in nature. They are the largest of the termite species, with some colonies reaching up to 10,000 members. They are distinguishable from other termites by their dark brown color and large size. Dampwood termites feed on decaying wood, and can cause significant damage to wooden structures if left unchecked. They are also known to feed on wood-based materials such as paper and cardboard. To prevent an infestation, homeowners should inspect their property regularly for signs of dampwood termites and repair any damaged wood.
Human Interaction with Termites
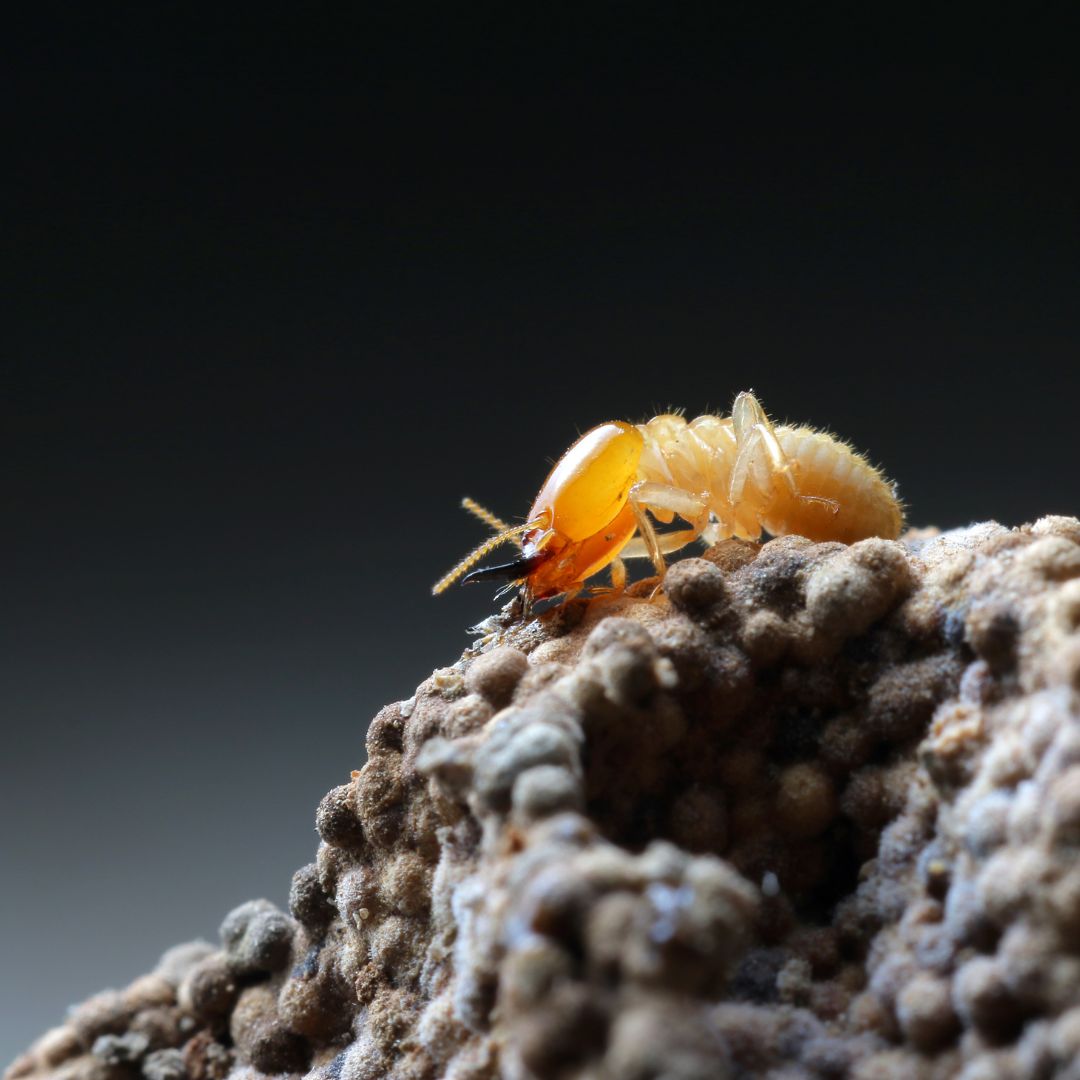

- Termites can cause significant structural damage to buildings and homes by eating through wood, paper, and other cellulose-based materials.
- Humans can take preventative measures to avoid termite infestations, such as using treated lumber for construction and using chemical barrier treatments to protect the soil around the foundation.
- Humans can also use baiting systems, which place cellulose-based bait in a station around the perimeter of the home. The termites are attracted to the bait and then poisoned by the bait.
- Humans can also use chemical sprays that are specifically designed to kill termites, although these can be dangerous to use and may be ineffective against certain species of termites.
- In some cases, humans may need to hire a professional exterminator to eradicate a termite infestation.
1 Subterranean Termites
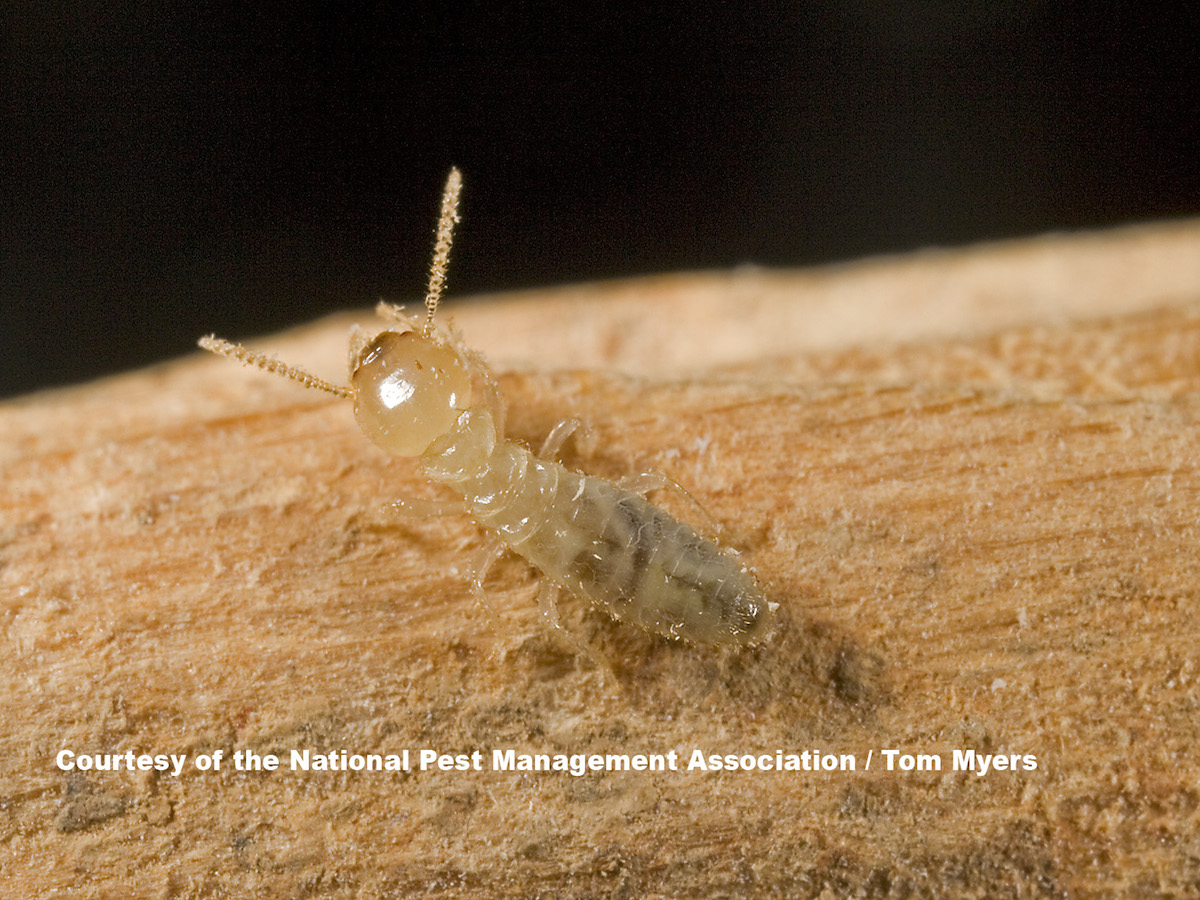
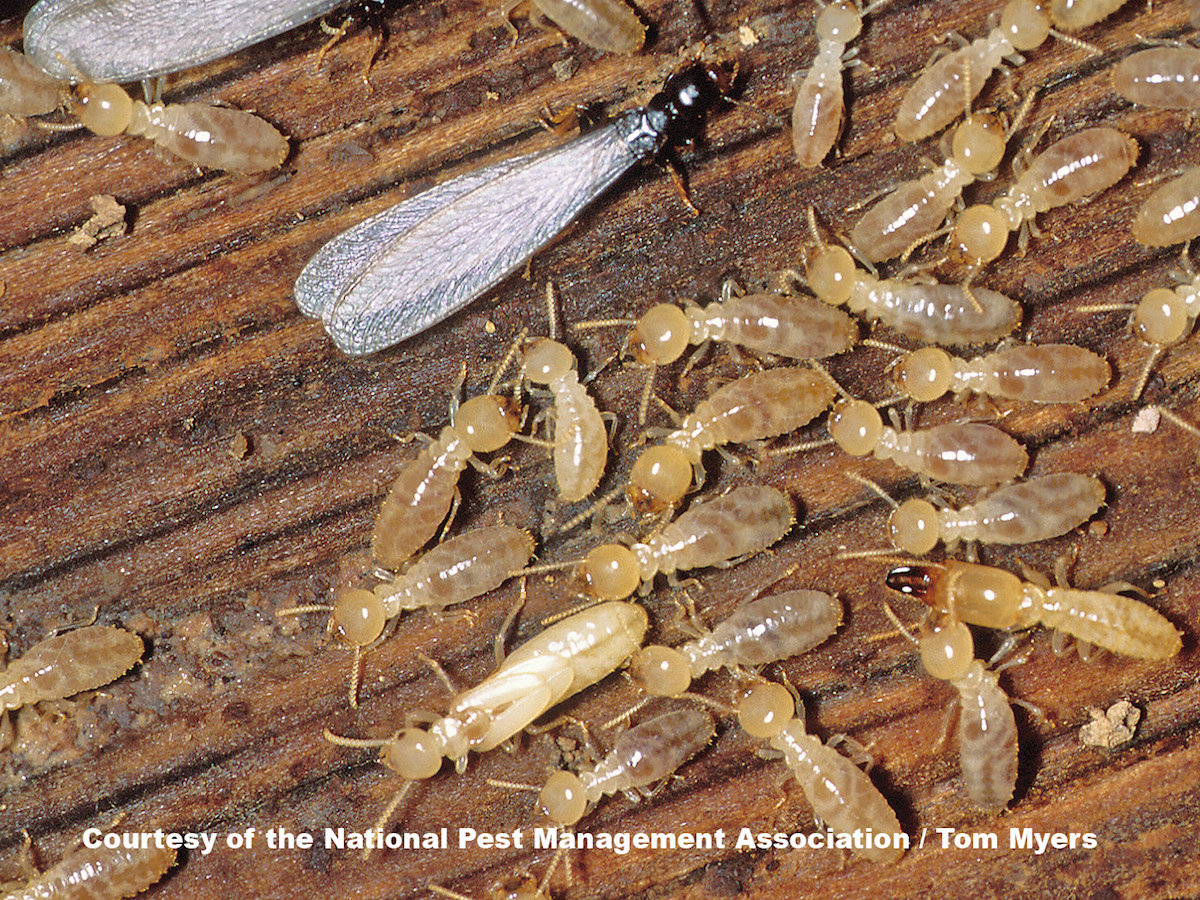
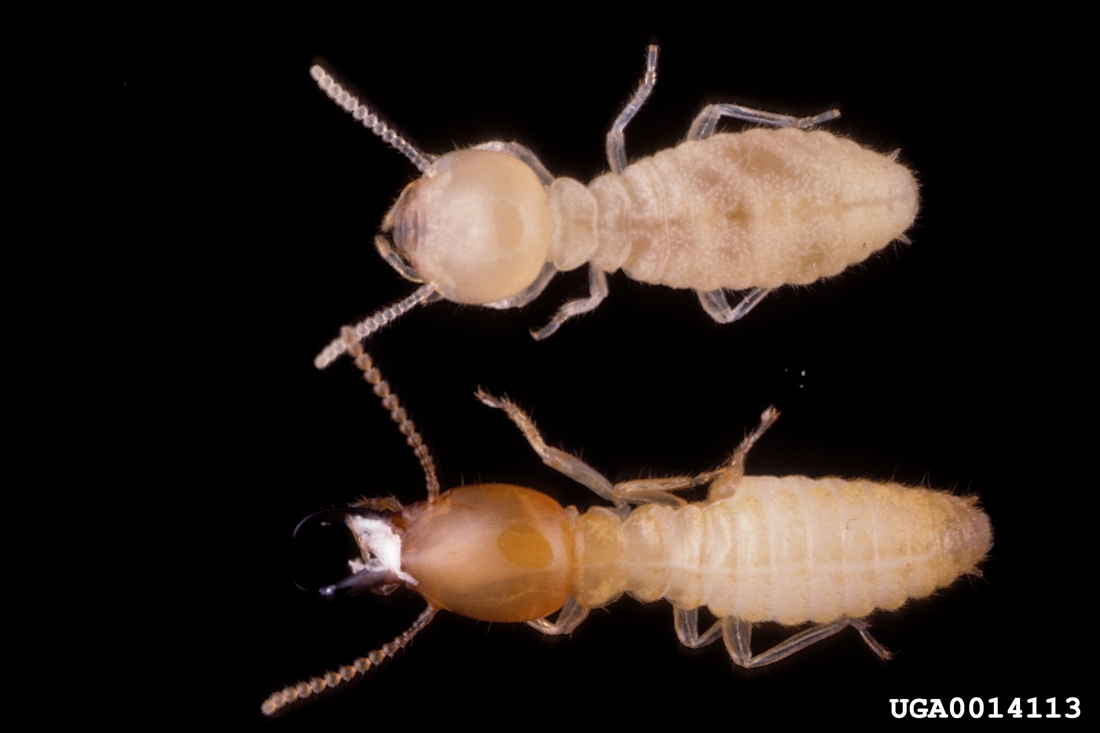



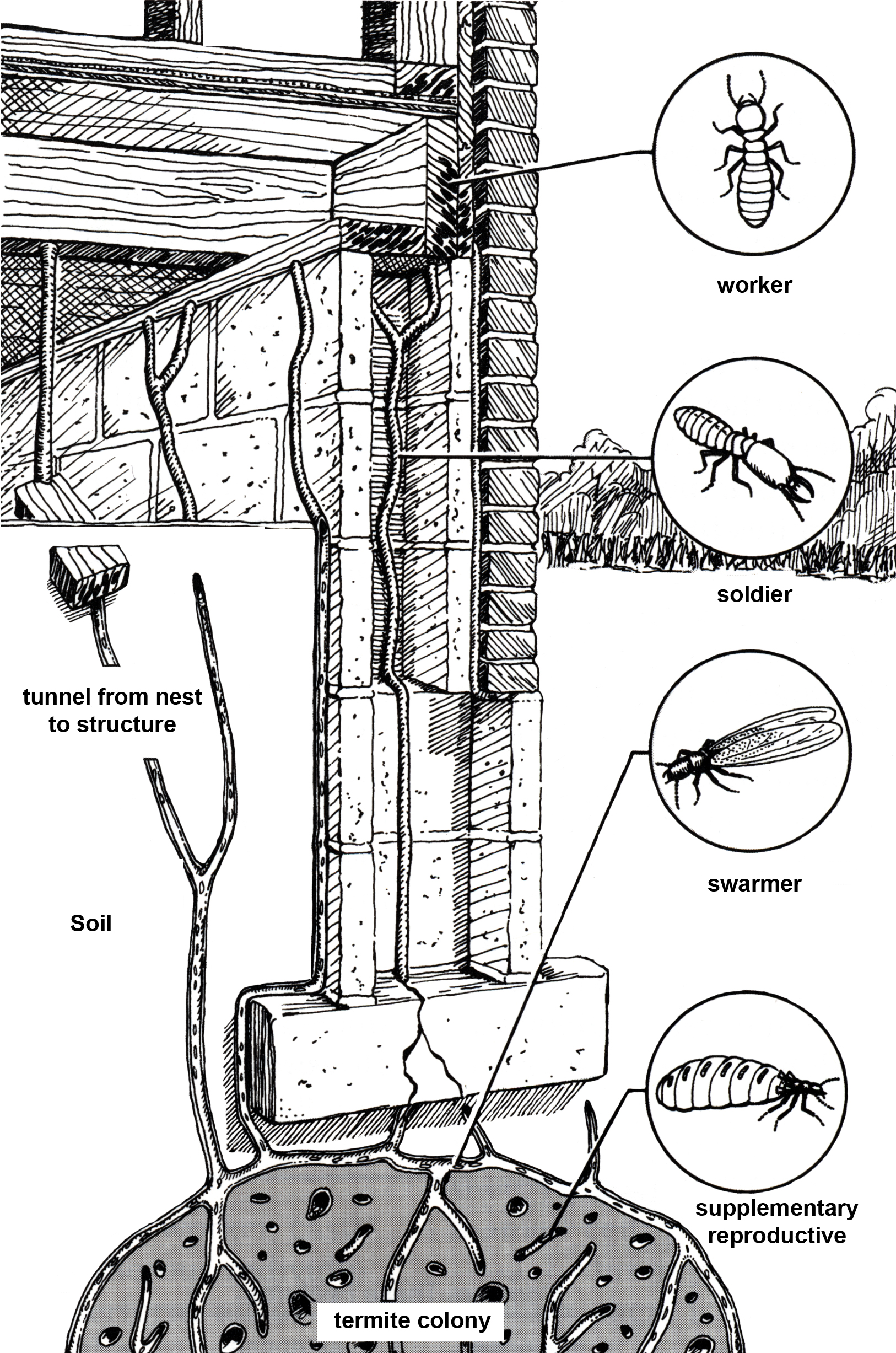
Subterranean termites are one of the most common type of termite found in the United States. They live in underground colonies and build mud tubes to access food sources. Subterranean termites need a moist environment to survive, so they travel through the soil or fly to find moist wood. They feed on cellulose found in wood, cardboard, and paper products. They are social insects that live in large colonies and are divided into three castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives. The workers are the smallest, cream-colored insects that do the majority of the work, while the soldiers have larger heads and darker bodies and protect the colony. Reproductives are dark brown or black and are responsible for reproduction in the colony.
2 Formosan Termites




- Formosan termites are native to China and Taiwan, and were introduced to the United States in the early 1900s.
- They are considered one of the most aggressive termite species, and are highly destructive to wooden structures and trees.
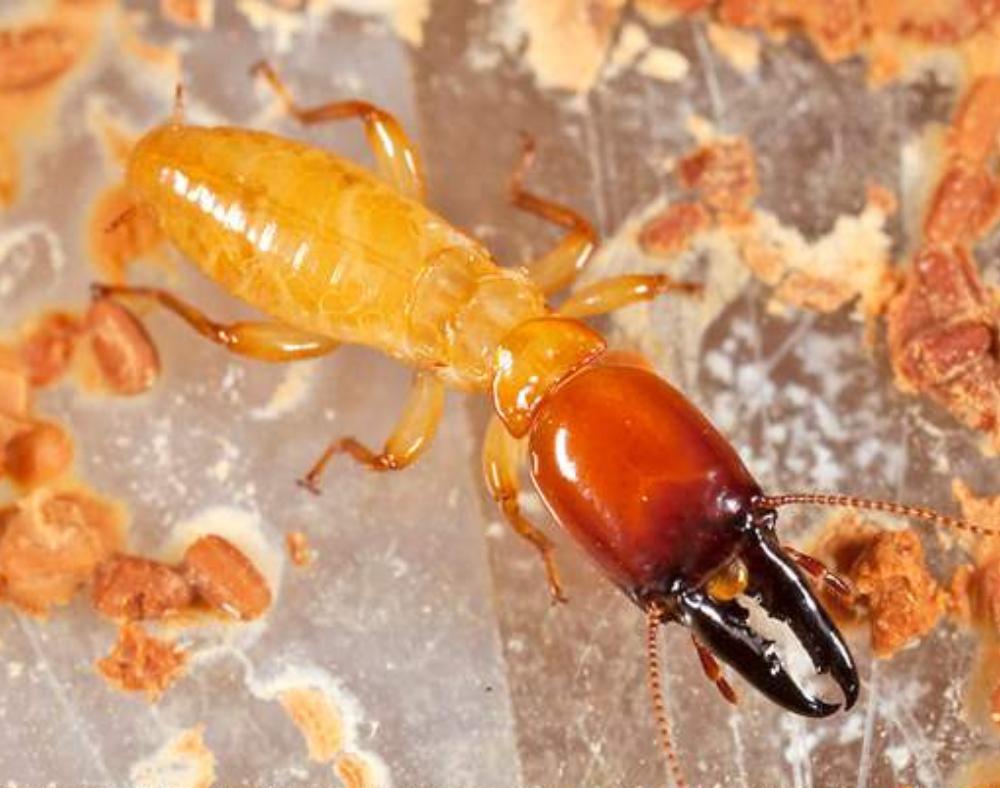
They are also known as “super termites” due to their ability to form large colonies that can cause extensive structural damage. Formosan termites have a voracious appetite, and they can consume up to 13 ounces (368 grams) of wood a day. They are also known to feed on other materials, including plastic, foam insulation, and fabrics. They can consume all of these materials in as little as three months.
3 Drywood Termites



- Dampwood Termites: These are the largest species of termites and they usually feed on wood that has high moisture content. They are usually found in moist and damp areas such as attics, crawl spaces and basements.
- Subterranean Termites: These are the most common type of termites and are found all over the world. They live in large underground colonies and feed on wood, paper and other materials. They can cause extensive damage to homes and buildings.
- Drywood Termites: These termites are found in dry and warm climates. They feed on dry wood and do not require any moisture to survive. They can cause significant damage to wooden structures and furniture.
4 Dampwood Termites



- Dampwood termites are usually found in decaying wood that has been exposed to high moisture levels.
- They are larger than other termite species, ranging in size from 1/2 to 3/4 of an inch.
- Dampwood termites prefer moist wood such as fence posts, window frames, and other structures that are near a water source.
- The presence of dampwood termites is usually indicated by the presence of large piles of sawdust and mud tubes that extend from the wood to the soil.
Control Measures
| Preventive Measures | Control Measures |
|---|---|
| Inspect your home regularly for signs of termite activity | Treat the affected area with appropriate insecticides |
| Check for moisture sources near your home and fix them | Install physical barriers like a metal sheet around or under your home |
| Check for wood-to-soil contact and fix it | Remove wood debris around the home |
| Store firewood away from your home | Set up baiting stations around the perimeter of your home |
Keep in mind that the most effective way to get rid of a termite infestation is to call a professional pest control service. They will be able to accurately diagnose the problem and identify the best solution.
1 Subterranean Termites



| Type | Origin |
|---|---|
| Subterranean Termites | Soil |
Subterranean termites are the most common type of termite and are found in every state in the United States except Alaska. They build their colonies in the soil and need moisture to survive. These termites build mud tubes to travel between their colonies and the structure they are infesting. They feed on cellulose-based plant materials, such as wood, paper, and cardboard. They are capable of causing significant damage to homes and buildings if left untreated.
2 Formosan Termites




| Common Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Formosan subterranean termite | Coptotermes formosanus |
| Asian subterranean termite | Coptotermes gestroi |
Formosan termites are a species of subterranean termites that are native to several areas in East Asia, including China, Taiwan, and Japan. They are among the most destructive species of termites, and are capable of rapidly damaging buildings and other structures. Formosan termites are divided into two species: the Formosan subterranean termite (Coptotermes formosanus) and the Asian subterranean termite (Coptotermes gestroi). Both species feed on cellulose-containing materials, such as wood, paper, and cardboard. They are known to build large colonies and can form mud tubes from the soil to their food sources. Formosan termites can be difficult to control and eradicate, and may require professional pest control services.
3 Drywood Termites



| Name | Size | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Conehead Termite | 1/2″ | Southern US |
| Desert Drywood Termite | 1/2″ | Southern US, Hawaii, Central America |
| Western Drywood Termite | 1/2″ | Southern US, Hawaii, Central America |
Drywood termites live in dry wood, such as homes and furniture, instead of underground. They build galleries and tunnels in the wood, which can cause significant damage over time. Three of the most common drywood termites include the Conehead Termite, the Desert Drywood Termite and the Western Drywood Termite.
The Conehead Termite is found in the southeastern United States and measures 0.5 inches long. It is yellow in color with a darker head. This is the most destructive of the three drywood species and they are commonly found in old, dry wood.
The Desert Drywood Termite is found in the southern United States, Hawaii, and parts of Central America. It is also yellow in color and measures 0.5 inches long. Desert Drywood Termites tend to feed on wood that is damp or humid and can be found in furniture or wooden structures.
The Western Drywood Termite is similar to the Desert Drywood Termite and is also found in the southern United States, Hawaii, and parts of Central America. It is also yellow in color and measures 0.5 inches long. Western Drywood Termites tend to feed on wood that is damp or humid and can be found in furniture or wooden structures.
4 Dampwood Termites



| Termite Species | Common Locations |
|---|---|
| Zootermopsis angusticollis | Pacific Northwest |
| Zootermopsis nevadensis | Pacific Northwest, California, Nevada, Idaho, and Utah |
| Zootermopsis laticeps | Southern California |
| Zootermopsis hageni | Oregon, Northern California |
Dampwood termites are a group of termite species that inhabit moist or decaying wood. The most common dampwood termite species are Zootermopsis angusticollis, Zootermopsis nevadensis, Zootermopsis laticeps, and Zootermopsis hageni. Zootermopsis angusticollis is commonly found in the Pacific Northwest, while Zootermopsis nevadensis is found in the Pacific Northwest, California, Nevada, Idaho, and Utah. Zootermopsis laticeps is found in Southern California, and Zootermopsis hageni is found in Oregon and Northern California.
Prevention & Management

| Prevention | Management |
|---|---|
|
|
Preventing a termite infestation is the best way to keep termites away from your home. This can be done by keeping wood piles away from the house, removing any damaged wood or debris, reducing moisture in and around the home, repairing any leaking pipes, and checking any wood products before purchasing them.
If an infestation has already occurred, there are several management strategies that can be used. Inspecting the home regularly and hiring a professional exterminator are the best ways to detect and treat the infestation. Chemical treatments and traps can also be used to help with existing infestations. Finally, infested wood should be removed and replaced.
1 Subterranean Termites



| Scientific Name | Reticulitermes spp. |
| Habitat | Lives in underground colonies, typically in soil, wood, or wall voids. |
| Diet | Feeds on cellulose, found in wood and wood products. |
| Appearance | Brown to yellowish-white in color, subterranean termites are the smallest of all termite species, measuring between 1/4 and 1/2 an inch in length. |
| Signs of Infestation | Mud tubes on the exterior of a building, swarms of winged termites emerging from the structure, or piles of discarded wings near doors or windows. |
Subterranean termites, scientifically known as Reticulitermes spp., are the most commonly found termite species in the US. They live in underground colonies, typically in soil, wood, or wall voids. Subterranean termites feed on cellulose, which is found in wood and wood products. They are brown to yellowish-white in color, and are the smallest of all termite species, measuring between 1/4 and 1/2 an inch in length.
Signs of an infestation include mud tubes on the exterior of a building, swarms of winged termites emerging from the structure, or piles of discarded wings near doors or windows.
2 Formosan Termites




- Formosan subterranean termites are the most destructive species in the world. They are native to China, Taiwan, and other parts of Southeast Asia.
- They cause approximately $1 billion in damage to structures in the U.S. every year. These termites have been accidentally introduced to new areas and can now be found in many parts of the world, including the U.S., Australia, and South America.
3 Drywood Termites



| Name | Type | Region |
|---|---|---|
| Cryptotermes brevis | Subterranean | Southern US, Caribbean, South America |
| Incisitermes minor | Drywood | Southwest US, Mexico, Central America |
| Incisitermes snyderi | Drywood | Southwest US, Mexico, Central America |
Drywood termites are among the most common species of termites. These termites are found in warmer climates, such as in the southeastern United States, the Caribbean, South America, Southwest US, Mexico, and Central America. They are known to infest dry wood, such as houses and furniture, and can cause extensive damage if left untreated. Some of the most common drywood termites are Cryptotermes brevis, Incisitermes minor, and Incisitermes snyderi.
4 Dampwood Termites



Dampwood termites are among the largest species of termites, and are found in humid coastal regions. They are typically found in wood that is already damp, such as fallen trees and stumps, and prefer to feed on wood with high moisture content. They require a high moisture content to survive, so they are rarely found in dry, desert climates. Dampwood termites are brown or black in color, and have long, straight antennae. They typically form colonies of several hundred to a few thousand individuals. They do not build tubes or other structures in order to travel from one food source to another, instead using their wings to fly in search of food. Dampwood termites are highly destructive to wood, consuming large amounts of it and causing extensive damage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Signs of a Termite Infestation?
Signs of a termite infestation can include the presence of mud tubes, damaged wood, and piles of discarded wings from swarming termites. Termites may also produce a distinct, musty smell throughout the house. Additionally, some species of termites cause a clicking noise, which can be heard coming from infested walls.
How do Termites Enter a Home?
Termites can enter a home through cracks in the foundation, small openings around pipes and other utilities, and even through the soil. They may also enter a home through wood-to-ground contact. Termites may also enter a home via firewood, mulch, or other wood sources that are brought in from outside.
What can be done to prevent a termite infestation?
To prevent a termite infestation, there are a few steps that can be taken. Homeowners should inspect the exterior of the home for any cracks or gaps in the foundation, as well as any areas where wood may be in contact with the soil. Seal any cracks or gaps, and replace any rotting wood. Additionally, reduce the amount of moisture in the home by fixing any leaky faucets or pipes, and ensure that gutters and downspouts are functioning properly. Inside the home, ensure that all wood is kept at least 6 inches off the ground, and reduce humidity levels. Lastly, remove any sources of food that may attract termites, such as wood or paper.
How do you identify the type of termite infesting your home?
The type of termite infesting your home can be identified by inspecting the type of damage caused, as well as the size and color of the termites. Drywood termites typically cause cubical-shaped holes in wood, with the resulting sawdust being very fine in texture. Subterranean termites create mud tubes, which are used to transport food and water to the colony. These tubes are typically found on the foundation walls of your home. Formosan termites are larger than average and are usually yellowish-brown in color. They can be found in both drywood and subterranean colonies. Identifying the type of termite infestation is important in order to choose the most appropriate treatment.
What are the Potential Dangers of a Termite Infestation?
Termite infestations can cause serious damage to a home or building, with the potential to cause extensive wood damage, weaken walls and foundations, and even cause structural collapse. Termites also pose a risk to furniture, books, carpets, and other items in the home. In addition, termites can cause allergic reactions in some people, and can also attract other pests and parasites.
Conclusion
Termites are social insects that live in colonies and feed on cellulose, the main component of wood. They are considered one of the most destructive pests in the world, causing billions of dollars in property damage annually. Their presence can be detected through the presence of discarded wings, mud tubes, and sawdust-like droppings. The origins of these pest invaders have been traced back to the tropical regions of South and Central America, from where they spread to other parts of the world. Termites are able to thrive in a variety of environments and can even survive underground. While their presence can be disruptive, there are a variety of methods available to help prevent and control them.