Termites are remarkable architects, constructing intricate and well-protected dwellings known as shelter tubes. In this article, we’ll explore the secrets of how these tiny insects construct their homes and the fascinating science behind their engineering feats.
What are Termites?
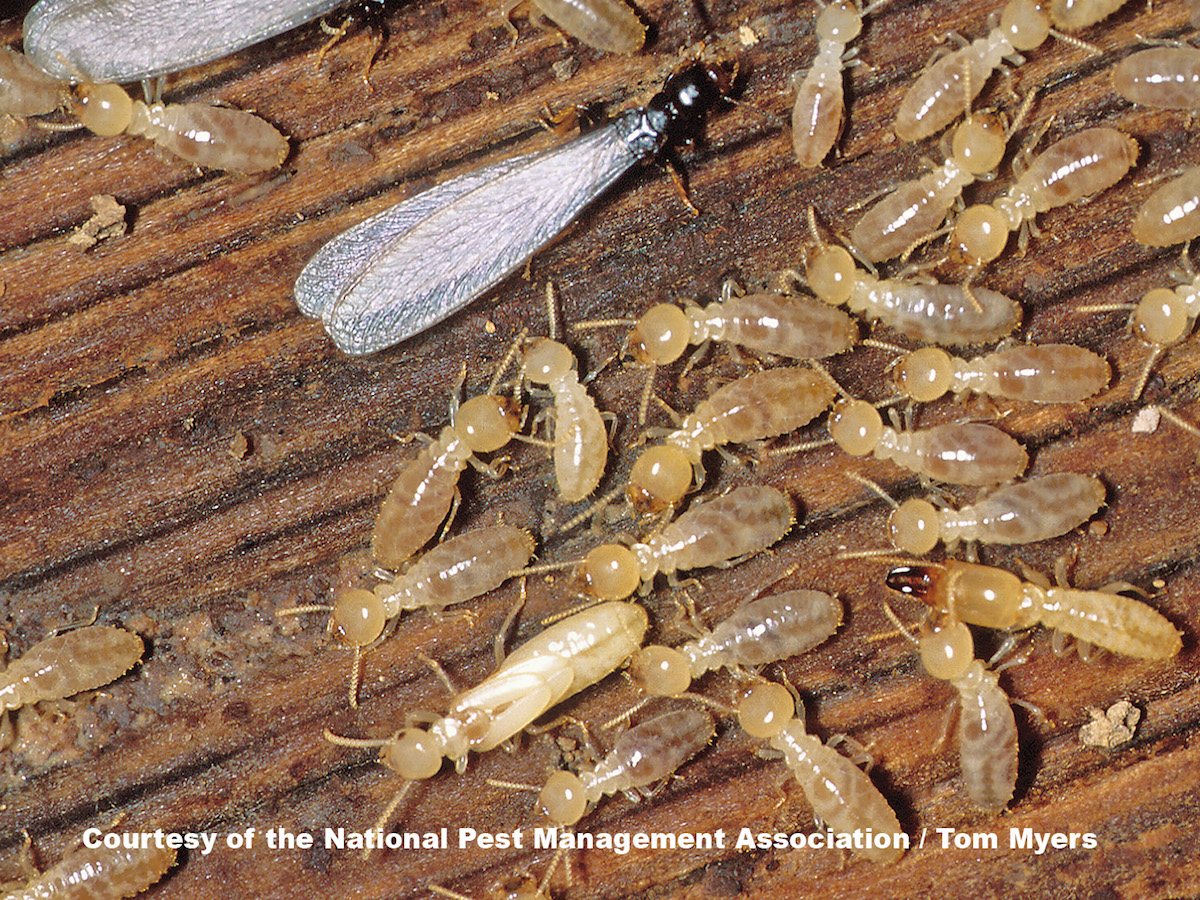

Termites are small, soft-bodied insects that feed on wood and are found in many parts of the world. They live in colonies and build complex underground tunnel systems called shelter tubes, which are used to protect them from predators and the elements. These shelter tubes can cause damage to wood structures and furnishings.
Types of Termites
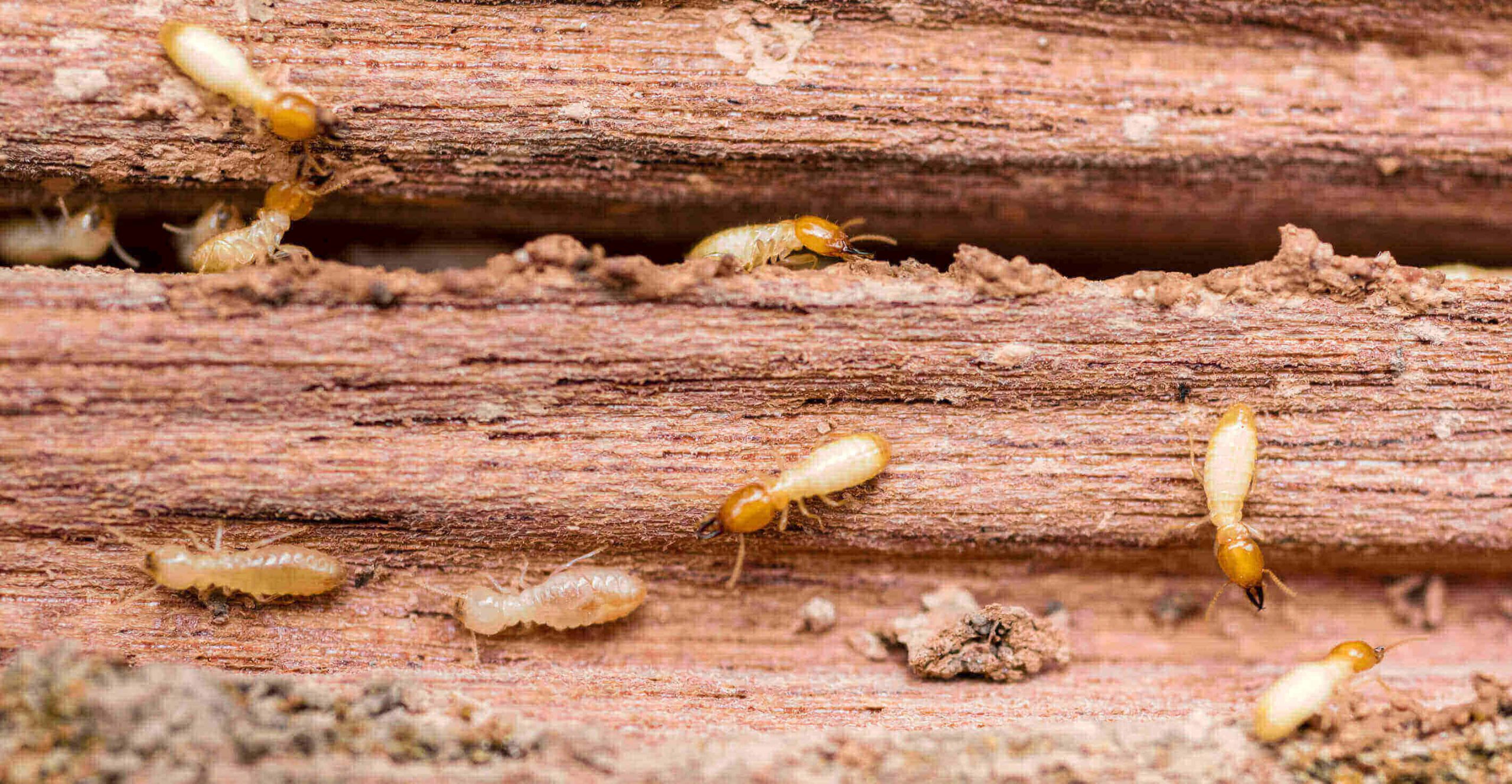

Termites are divided into three major categories: dampwood, drywood and subterranean. Dampwood termites are found in dead, damp wood, hence their name. They are also known as ‘rotten wood’ termites, as they feed on decaying wood. Drywood termites prefer to feed on dry wood, and are often found in furniture, doorframes and windowframes. Subterranean termites live in the soil and require contact with the ground to survive. They build elaborate shelter tubes to protect themselves from the environment.
What are Shelter Tubes?
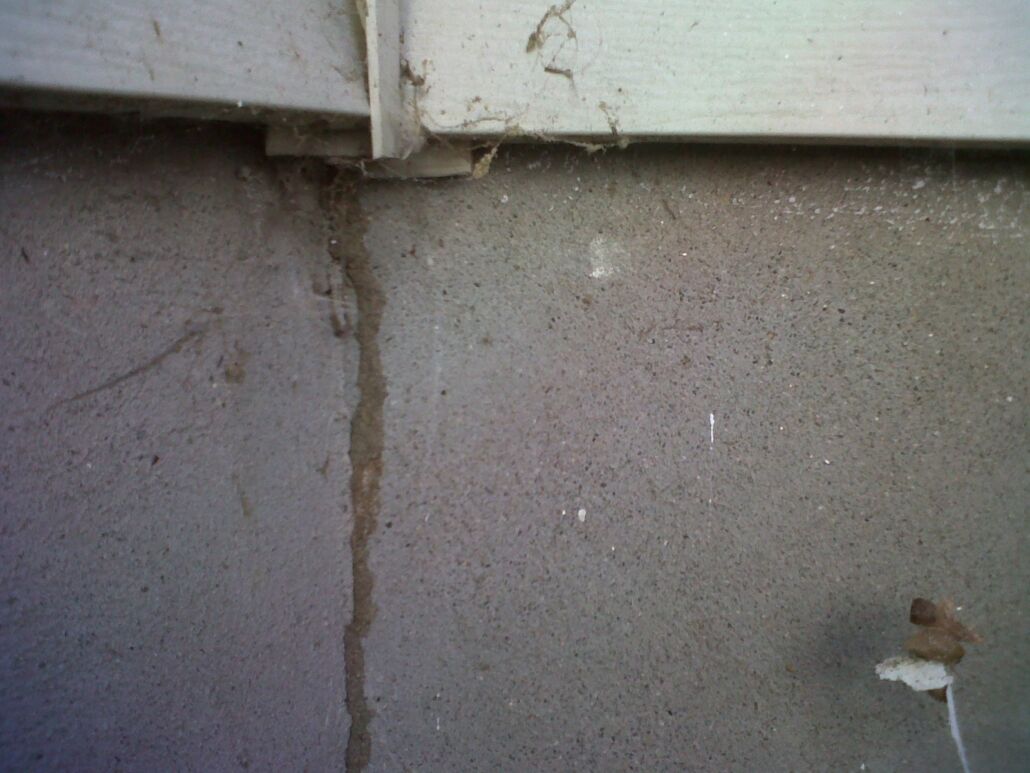

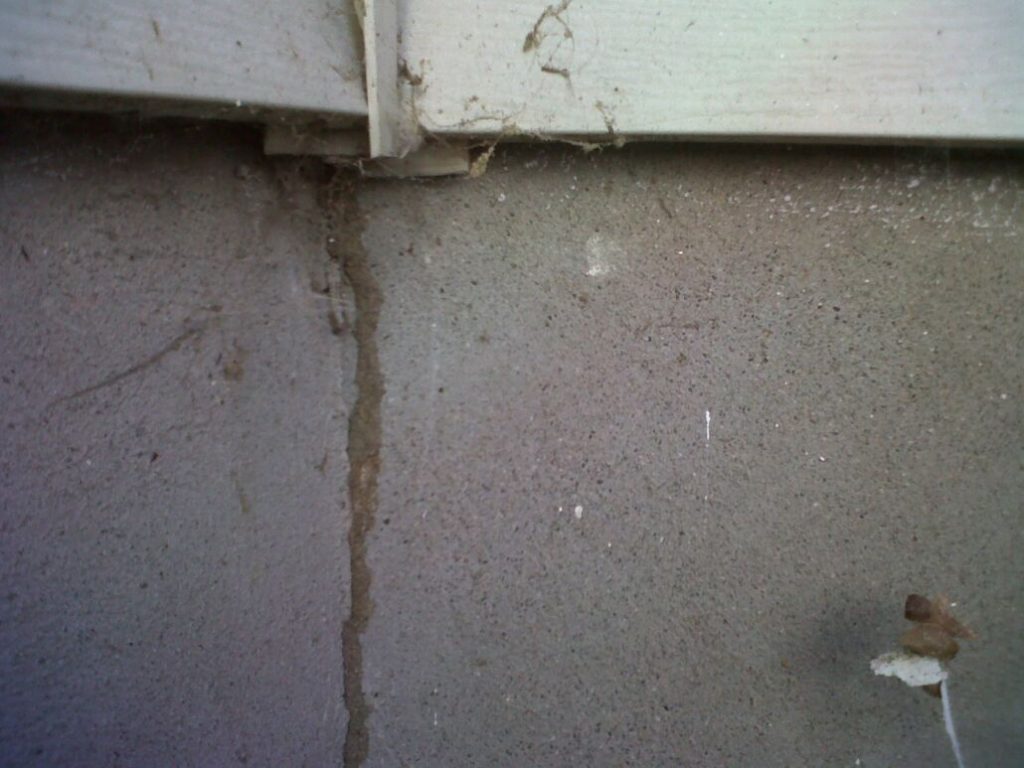
Shelter tubes are structures made of soil, wood and other debris formed by subterranean termites as they travel between their colony and a food source. They provide a protected path for the termites to move safely between the two locations, and they are often seen on the exterior walls of homes. The tubes are typically made from particles of soil, small pieces of wood and other debris, and are held together by the saliva and excrement of the termites.
The tubes can be up to several inches in diameter and can reach up to 20 feet in length. They are usually found on walls, foundations, and other vertical surfaces, and may be found around windows and doors. They can also be found above ground, in the form of mud tunnels, which are created when the termites find a food source above ground.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Material | Soil, wood and other debris |
| Size | Up to several inches in diameter and up to 20 feet in length |
| Location | Exterior walls, foundations, windows and doors |
| Above Ground | Mud tunnels |
How Do Termites Build Shelter Tubes?
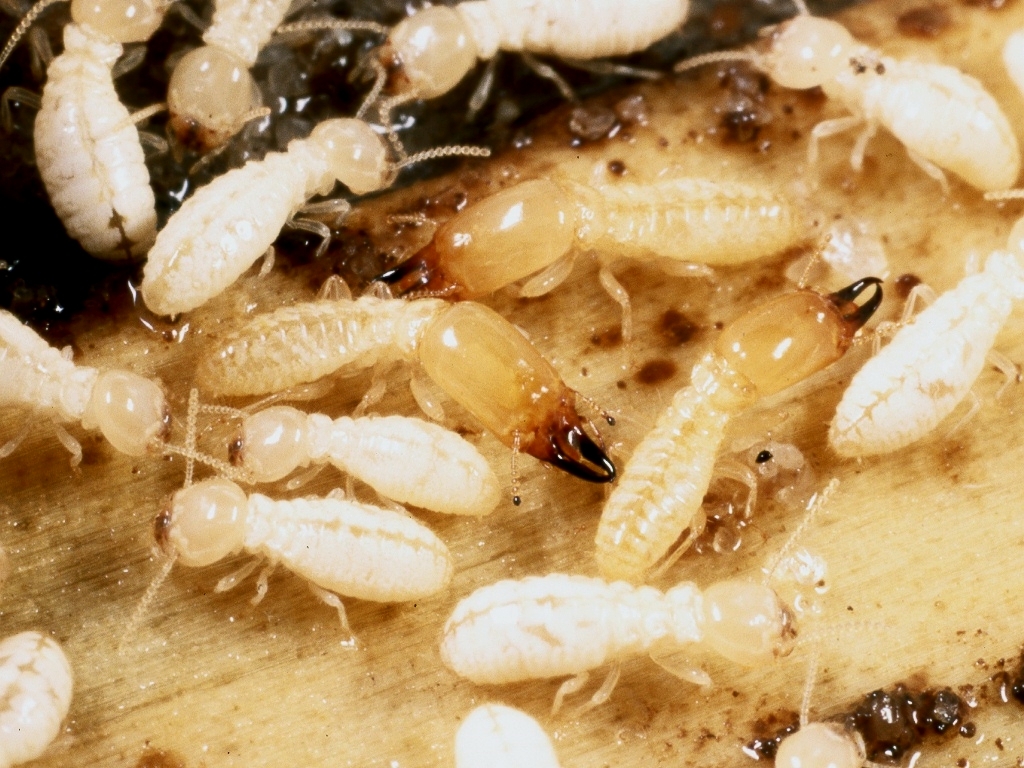

Termites are social insects who build their homes in the form of colonies. They build shelter tubes to protect themselves from heat, drought and predators. These tubes are constructed using soil, saliva, and excrement. The saliva acts as a binding agent to the soil and other particles, while the excrement helps to moisten the mixture.
The termites begin by excavating the soil within the colony and forming a mound. They then construct the shelter tubes by forming a thin, continuous line of the soil mixture around the mound. The shelter tubes are usually a few inches thick and can extend several meters in length.
The shelter tubes are typically built in dark, humid areas of the colony, such as beneath wood, in cracks and crevices, and around the edges of the mound. The tubes are then used to reach food sources and to move around the colony. The termites may also use the shelter tubes to enlarge their colony, as they can extend the tubes to other locations.
Termites also use the shelter tubes to protect themselves from predators and extreme temperatures. The tubes act as a barrier between the colony and the outside environment and keep the termites safe from the elements and predators. Additionally, the shelter tubes provide the termites with an additional layer of insulation, keeping the interior of the colony at an optimal temperature for the termites.
In summary, termites build shelter tubes to protect their colonies from the elements and predators. The tubes are created using soil, saliva, and excrement, and are typically built in dark, humid areas of the colony. The tubes are also used to reach food sources and to move around the colony. Finally, the shelter tubes provide the termites with an additional layer of insulation, keeping the interior of the colony at an optimal temperature.
Benefits of Shelter Tubes
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Protection | Termites build shelter tubes to protect themselves from predators and environmental stress. |
| Moisture Regulation | The shelter tubes act as a barrier against dry air and allow the termites to remain protected, while still providing them with the moisture they need to survive. |
| Environmental Conditions | The tubes also provide an ideal environment for the termites to live in, as they are designed to maintain optimal temperature and humidity levels. |
| Food Supply | The shelter tubes are also used to provide the termites with a source of food, as the tunnels can be used to bring food to the nest. |
Shelter tubes are an essential part of the life cycle of termites, as they are used for many different purposes. The tubes provide protection from predators and environmental stress, regulate moisture levels, and provide an ideal environment for the termites to live in. Additionally, the shelter tubes are also used as a food supply, as they can be used to bring food to the nest.
Different Types of Materials Used for Building Shelter Tubes

- Soil
- Pebbles
- Sawdust
- Wood chips
- Sand
- Cement
- Gravel
- Mud
- Moss
- Leaves
Termites use a variety of materials to build their shelter tubes. These materials include soil, pebbles, sawdust, wood chips, sand, cement, gravel, mud, moss, and leaves. These materials are carefully chosen by the termites and carefully packed together in order to provide a safe, protected environment for the termite colony. These shelter tubes also help protect the termites from predators and the elements.
How Long Does it Take for Termites to Build Shelter Tubes?
Termites build shelter tubes in order to travel between their nest and food sources. Shelter tubes are made of mud and saliva and can provide protection from predators. The time it takes for termites to build shelter tubes depends on the species of termite and the size of the shelter tube.
Subterranean termites, which are one of the most destructive species of termites in North America, construct shelter tubes in about one week. Drywood termites, which are found in warmer climates, are slower to build shelter tubes, which can take up to two weeks.
The size of the shelter tube can also affect the time it takes for termites to build it. Smaller tubes can be constructed in a few hours, while larger tubes may take several days or even weeks.
In addition to the time it takes to build the shelter tube, termites must also spend time gathering the materials necessary to make the tube. This may include mud, saliva, and other materials that help the tube hold its shape.
Once the shelter tube is finished, it serves as a protective structure for termites as they travel back and forth between the nest and food source. The shelter tubes also help keep them hidden from predators and the elements.
In conclusion, the time it takes for termites to build shelter tubes can vary from a few hours to several weeks, depending on the species of termite and the size of the shelter tube.
Signs of Shelter Tubes
- Appearance of mud tubes, usually measuring up to 1 cm in diameter, on the exterior walls or foundation of the house.
- Presence of small holes in wooden structures and furniture, indicating termites have already infiltrated.
- Seeing swarmers (winged termites) around the house or in the vicinity of infested wooden structures.
- Presence of discarded wings near doors and windows.
- Damp or soft wood in the house, indicating that termites may have fed on it.
- Discoloration of the wood and bubbling of the paint on walls, indicating moisture build-up due to termites.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do termites build their shelter tubes?
Termites build their shelter tubes by using their saliva and mud to construct a tunnel from their nest to a food source. They start by secreting a sticky substance from their mouths that acts as a glue for the mud. They then use their heads and mouths to move the mud and form the shelter tube. Once the shelter tube is complete, the termites will use their saliva to seal any cracks or openings in the tube. This helps to protect the termites from predators and keep their nest area safe and secure.
What materials do termites use to construct mud tubes?
Termites construct their mud tubes primarily from soil, saliva, and feces. They use their jaws and antennae to mix the materials together, and then use their mandibles to form the tubes. The tubes provide the termites with a protected environment as they travel through the air and over open surfaces. The tubes also provide insulation and humidity, aiding the termites in regulating their body temperature.
How do termites use mud tubes to protect themselves?
Termites use mud tubes to protect themselves from predators, such as ants and birds, as they travel between their nest and the food source. The mud tubes also help to regulate the temperature and humidity for the termites. The tubes are made from soil and saliva that the termites mix together, and then apply to the surfaces they are travelling on. The mud tubes provide the termites with a safe and secure environment, allowing them to travel between their nest and food source without fear of being eaten.
What is the purpose of mud trails left by termites?
Mud trails left by termites are used as a way of communication between different termite colonies. The trails are used to mark their territory, as well as to locate food sources. They also provide a way for the termites to transport food, moisture, and other materials. The trails also serve as a protective barrier from predators and other environmental threats.
How long does it take for termites to build mud tubes?
Termites build mud tubes which act as a shelter and provide moisture for them. This process usually takes anywhere from a few days to a few weeks, depending on the size of the colony and the environmental conditions. The time taken for the termites to build the tubes also depends on the availability of materials such as soil and moisture. The mud tubes are usually built close to the ground and can be up to several feet long.
Conclusion
Termite shelter tubes are a remarkable construction feat. In a few days, termites can build complex structures made of mud and saliva that are strong and waterproof enough to protect the colony from the elements. Through a combination of collective behavior and individual decisions, termites are able to build efficient and secure homes that are key to the survival of the colony. Understanding how termites build their homes can provide insight into the evolution of architecture and construction in nature.