Did you know that termites are some of the most industrious creatures on the planet? These tiny insects have an amazing range of abilities and skills that put them in a class all their own. In this article, we’ll uncover some amazing fun facts about termites that you won’t believe.
Overview of Termites

Termites are small, primitive insects that are closely related to cockroaches and belong to the order Isoptera. They live in colonies and feed on wood, dead leaves, soil, animal dung, and other organic matter. There are over 3,000 known species of termites, which are found in tropical and subtropical regions across the world. In the United States, they can be found in the south and south-eastern regions. Termites are divided into three main groups: subterranean, drywood, and dampwood. Subterranean termites live in underground tunnels and build nests in wood. Drywood termites live in wood and don’t need contact with the soil. Dampwood termites live in decaying wood near the ground or in contact with soil, and are rarely found in homes. Termites are social insects, living in large colonies that can consist of millions of individuals. They have a caste system, with three distinct roles: workers, soldiers, and reproductives. The workers are responsible for feeding the colony, and are the most numerous; the soldiers protect the colony from predators; and the reproductives are responsible for reproduction.
Facts about Termites
- Termites are found in every continent except Antarctica.
- Termites are a major agricultural pest, causing an estimated $40 billion in property damage and crop losses annually.
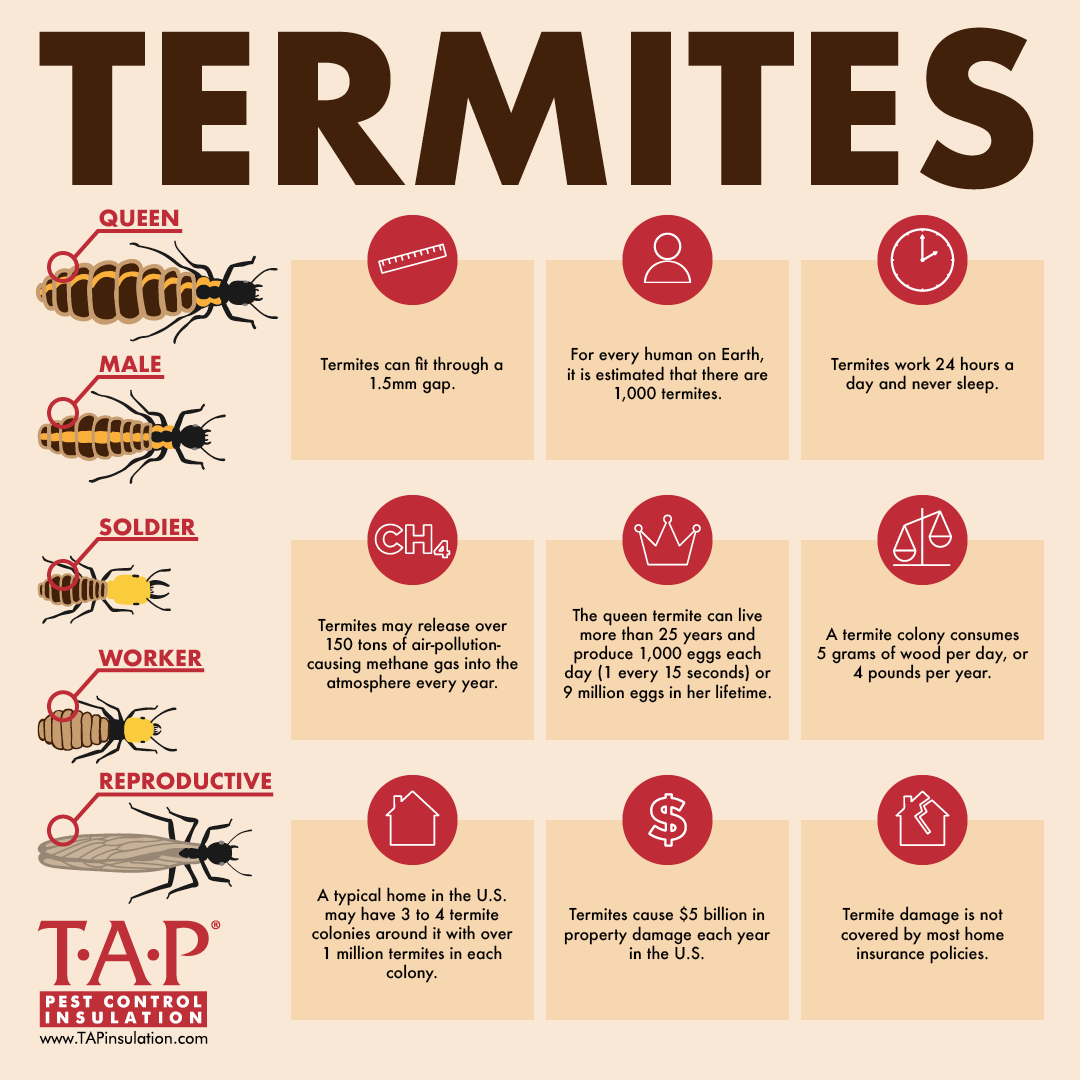
- Termites are social insects that live in colonies and are divided into three castes: workers, soldiers, and reproductives.
- Termites feed primarily on wood, but they can also consume paper, cloth, and other materials.
- Termites are blind, relying on their sense of touch and smell to navigate their environment.
- Termites are capable of producing sounds, though they are too low for humans to hear.
- Termites can live up to five years, with the queen living up to 15 years.
- Termites are capable of generating enough heat to keep their nests at a constant temperature.
- Termites consume about 8 pounds of wood per year per termite.
- Termites are an important part of the ecosystem, breaking down dead trees and returning nutrients to the soil.
Types of Termites
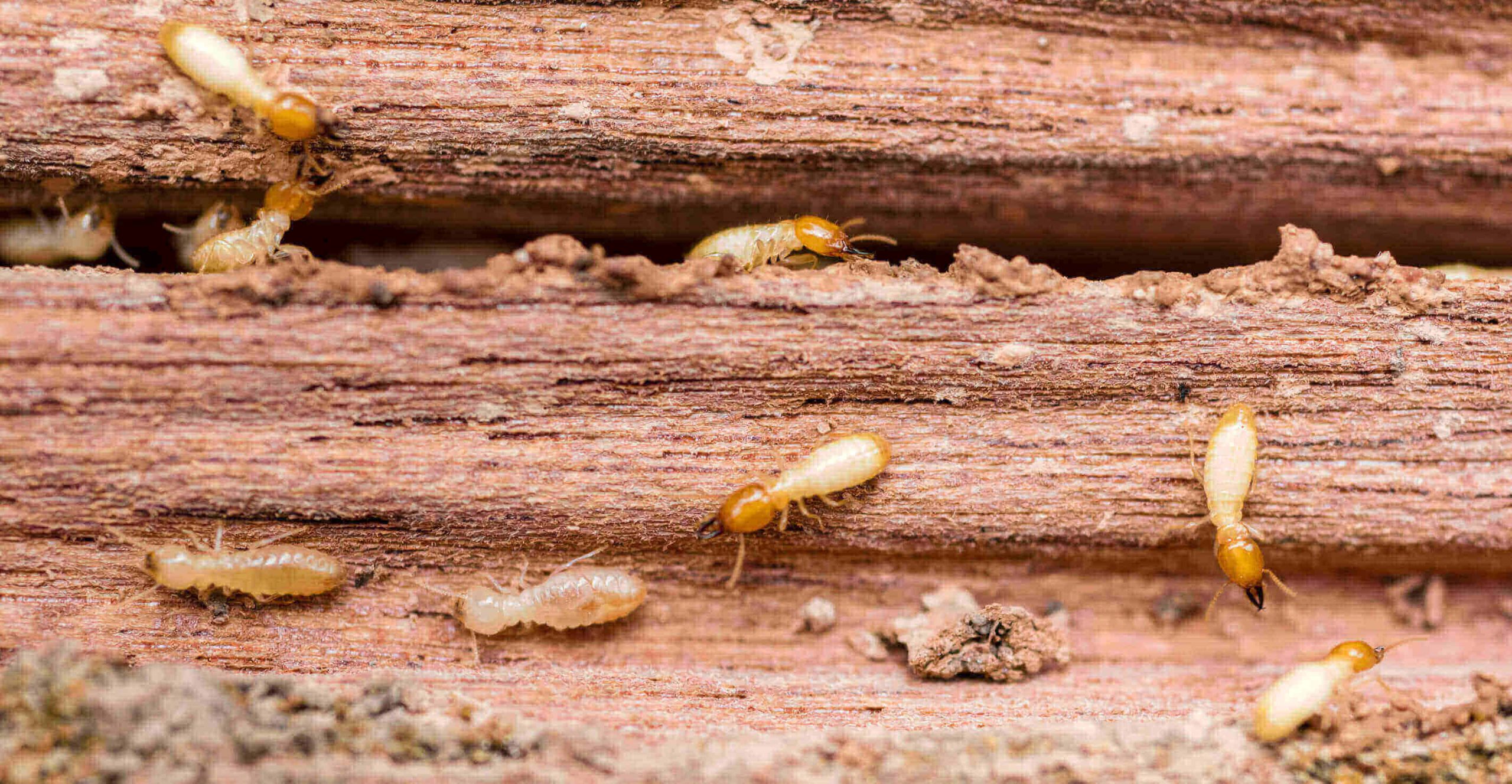

Termites are classified into three main categories: dampwood, drywood, and subterranean. Dampwood termites are usually found in moist wood, such as rotting tree stumps or logs, and typically build their nests in wood that is in contact with soil. Drywood termites are found in dry wood, such as framing lumber, furniture, and other wooden items, and generally infest wood without contact with soil. Subterranean termites live in the soil, and build mud tubes and tunnels to reach their food sources. They are the most destructive and widespread of the three types and are responsible for most of the damage caused by termites.
Diet of Termites

Termites are mainly herbivorous, consuming wood, grasses, leaves, and other plant material. They also consume fungi and soil, scavenge for dead plants and animals, and may even eat solid waste. The diet of termites mainly depends upon their specific species.
| Species | Diet |
|---|---|
| Subterranean | Wood, grasses, fungi, and soil |
| Drywood | Wood and other plant material |
| Dampwood | Dead plants and animals, fungi, and soil |
| Conehead | Living and dead plants, fungi, and soil |
Subterranean termites feed on wood, grasses, fungi, and soil, while drywood termites feed on wood and other plant material. Dampwood termites feed on dead plants and animals, fungi, and soil. Conehead termites feed on both living and dead plants, fungi, and soil. Some species of termites may even eat solid waste.
Habitat of Termites

Termites can be found in every continent except Antarctica. They live in diverse habitats such as deserts, grasslands, forests and urban areas. The most common type of termites are subterranean termites, which build nests in soil and feed on wood.
| Habitat | Location |
|---|---|
| Subterranean | Soil |
| Drywood | Wood |
| Arboreal | Trees |
| Desert | Deserts |
| Grassland | Grasslands |
| Forest | Forests |
| Urban | Urban Areas |
Subterranean termites form the largest group and are found in most regions of the world. Drywood termites inhabit dry wood and usually infest dead trees, buildings, and furniture. Arboreal termites live in trees and other wooded areas. Desert termites are found in desert climates, while grassland and forest termites live in grasslands and forests, respectively. In urban areas, termites may be found in houses and other man-made structures.
Lifecycle of Termites
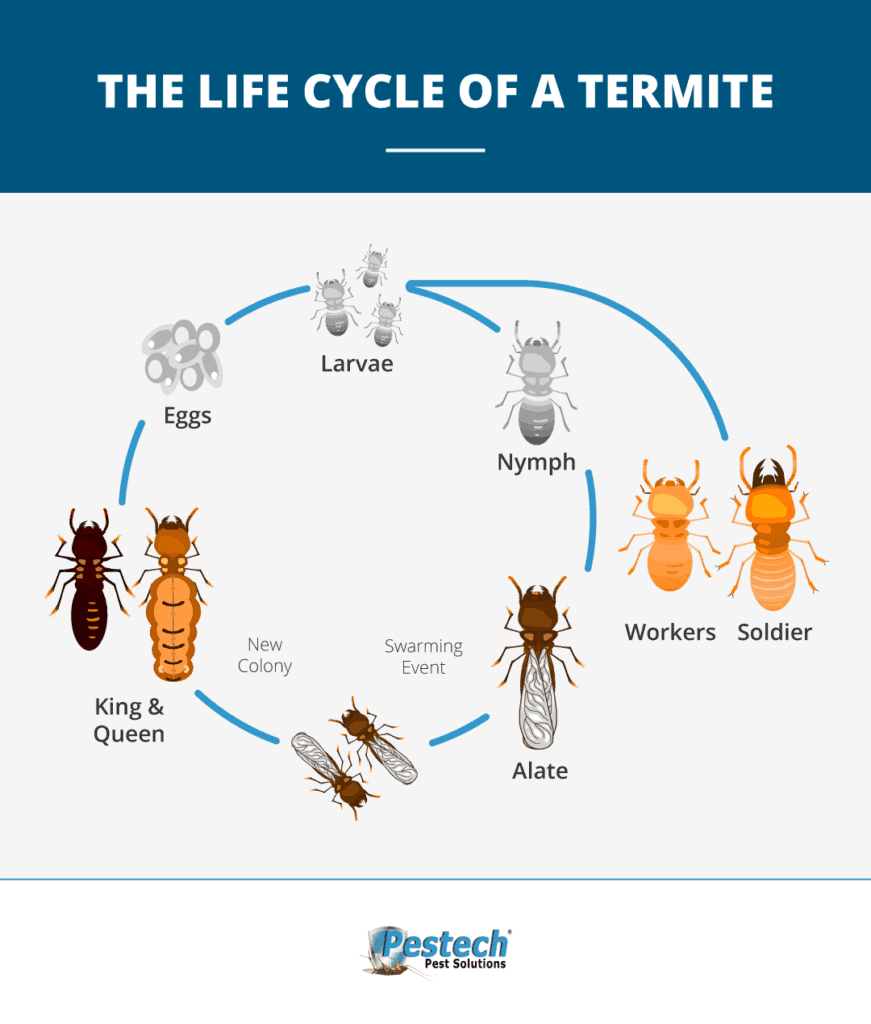
Termites undergo a complete metamorphosis, meaning they experience four distinct stages of development; egg, nymph, soldier, and reproductive. The eggs are laid by the queen, who may lay up to 2000 eggs per day. The eggs hatch after a few weeks and the nymphs then molt several times over several months to reach adulthood, which is usually within a year. The soldiers are the protectors of the colony and they have large, curved mandibles that they use to defend the colony from intruders. The reproductives are the queens and kings and they are the only ones capable of reproducing. Queens can live for up to 25 years and are capable of laying millions of eggs during their lifetime. The kings, on the other hand, only live for a few years and their sole purpose is to mate with the queen.
The Social Structure of Termites
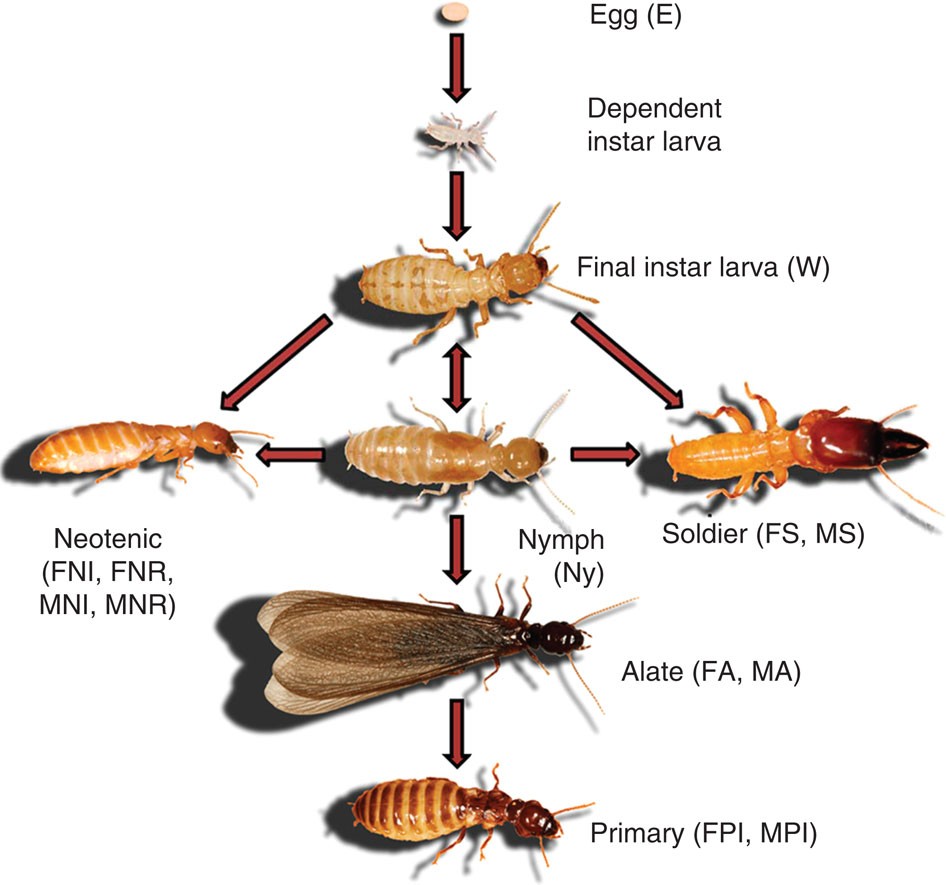
Termites live in colonies and have a highly organized and complex social structure. Each colony contains a queen, a king and a caste system of termites with different roles. This caste system is made up of workers, soldiers and reproductive members.
| Caste | Role |
|---|---|
| Queen | Reproductive female |
| King | Reproductive male |
| Workers | Gather food, build and repair nest, care for young |
| Soldiers | Defend the colony |
| Reproductive | Produce offspring |
The queen is the most important member of the colony and is responsible for producing most of the colony’s eggs. The king is the secondary reproductive and usually mates with the queen. The workers are the most numerous caste and are responsible for many of the colony’s activities, such as gathering food, building and repairing the nest, and caring for the young. The soldiers are the defenders of the colony and are responsible for protecting it from predators. The reproductive caste contains the reproductive members that produce the next generation of termites.
Symbiotic Relationships of Termites
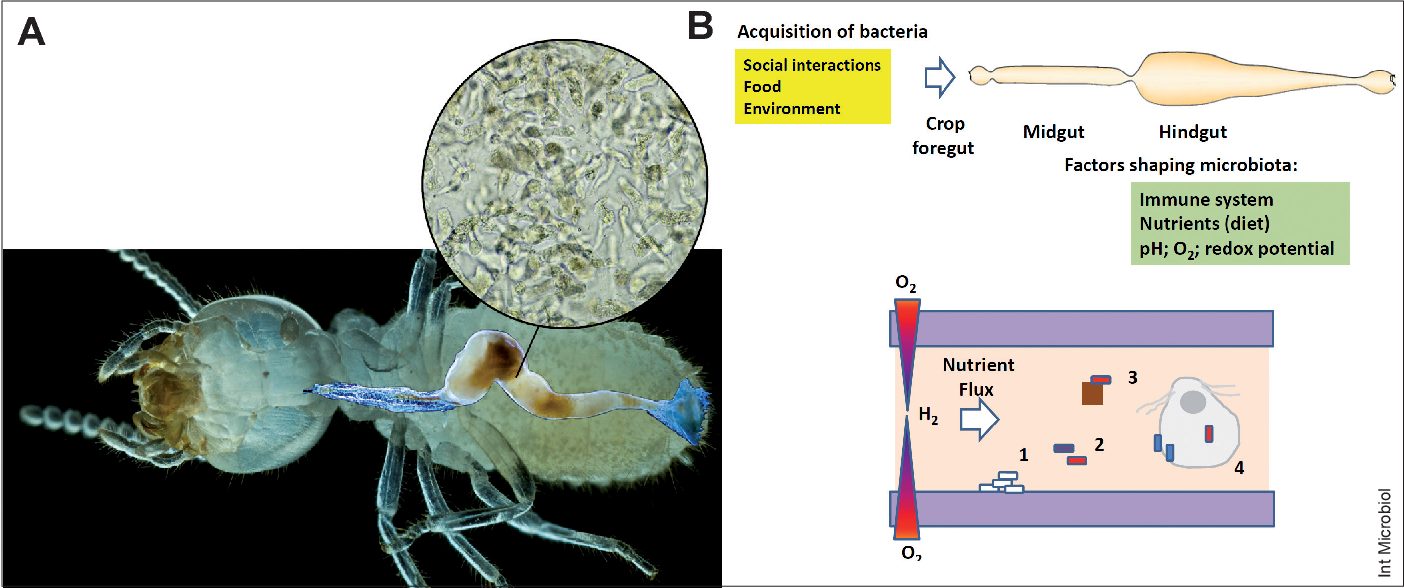
Termites are known to have various types of symbiotic relationships with other species, such as:
| Symbiont | Relationship with Termites |
|---|---|
| Bacteria | The bacteria in termites’ gut helps them digest cellulose and other plant matter. |
| Fungus | The fungus in termites’ gut helps them break down lignin, a tough material found in plant cell walls. |
| Protozoa | Protozoa in termites’ gut helps them digest cellulose, and can also provide them with essential amino acids. |
| Mites | Mites living on the termites’ bodies help groom them and remove debris. |
| Flies | Flies help termites find new food sources and can also act as scouts. |
| Ants | Ants help termites defend their colonies and can also provide them with food. |
Termites rely heavily on these symbiotic relationships to help them survive and thrive in their environment.
Interesting Behaviors of Termites
Termites are one of the most fascinating insects in the world. They have some unique behaviors that distinguish them from other insects. Here are some of the most interesting behaviors of termites:
• Termites have a complex social structure and communicate through chemical signals called pheromones. This allows them to divide labor, cooperate on tasks, and defend their colonies.
• Termites are masters of construction. They build intricate tunnels and mounds that can reach up to 30 feet high.
• Termites are good at adapting to their environment. They can build their nests in the ground, in trees, and even in the walls of human homes.
• Termite colonies are composed of different castes, such as workers, soldiers, and reproductive adults. Each caste has specific roles and responsibilities within the colony.
• Termites are highly efficient eaters. They can consume wood, paper, and other materials that are difficult for other insects to digest.
• Termites can survive in extreme temperatures, ranging from very cold to very hot.
• Termites can survive in waterlogged soils. This allows them to thrive in damp, humid environments.
• Termites are able to recognize their kin and make sure that they don’t attack or eat them.
• Some species of termites, such as the African Matabele ant, can form huge, densely packed colonies of up to 20 million individuals.
Understanding these behaviors of termites can help us better understand and appreciate these unique insects.
The Impact of Termites on Humans
- Termites are considered to be one of the most destructive pests in the world, causing billions of dollars in damages to structures and crops each year.
- Termites cause structural damage to buildings by eating away at wood, paper, and other materials used in construction.
- Termites can also cause damage to crops by directly consuming plants, or indirectly through the destruction of their roots and other parts of the plant.
- Termites can also cause health problems for humans by spreading diseases and causing allergic reactions.
- Termites also cause an increase in air pollution due to the release of methane gas as they consume wood and other materials.
Frequently Asked Questions
What amazing facts can be uncovered about termites?
Termites are social insects that live in large colonies and are a major player in the recycling of wood and plant matter. They have a unique relationship with certain species of fungi that help them digest cellulose. Termites can cause significant damage to wooden structures, yet they are also a key part of maintaining healthy ecosystems. Here are some amazing facts about termites:
• Termites have been around for over 250 million years!
• Termites can cause hundreds of billions of dollars in damage each year.
• Termites can inhabit a wide range of habitats, from deserts to rainforests.
• Termites are essential for the breakdown of dead plant matter and recycling of essential nutrients back into the soil.
• Termites can be used to detect the presence of certain pollutants in the environment.
• Termites have a complex social structure that includes queens, workers, and soldiers.
• Termites have an incredibly efficient digestive system that helps them break down hard-to-digest cellulose.
• Termites are sensitive to changes in their environment and can be used as indicators of environmental health.
How do termites survive in the wild?
Termites survive in the wild by feeding on wood, leaves, and other plant material. They are social insects that live in large colonies and work together to build intricate mounds and tunnels underground. They also feed on dead and decaying wood, which helps them to survive in the wild. Termites play an important role in the ecological balance of an environment by breaking down dead wood, helping to recycle essential nutrients in the soil.
What remarkable abilities do termites possess?
Termites possess remarkable abilities such as the ability to detect moisture, build complex and intricate structures, and communicate and cooperate with each other. They have been observed building towers and mounds that can reach up to 30 feet in height, and they have even been found to use their feces to create pathways to water sources. Termites also have complex digestive systems which enable them to digest wood, making them a major agricultural pest. Finally, the communication abilities of termites are astonishing; they use pheromones and other signals to communicate and even forage for food.
How do termites benefit the environment?
Termites play an important role in the environment by breaking down dead wood and other plant material, which helps to recycle essential nutrients back into the soil. This process, known as decomposition, is essential for healthy ecosystems, as it helps to keep the soil fertile and provides food for other organisms. Termites are also important food sources for many animals, including birds, reptiles, and mammals.
How can humans protect their property from termites?
The best way to protect property from termites is to use preventive measures such as using termite-resistant materials, sealing or closing off potential entry points, and keeping soil and vegetation away from the foundation. Other preventive steps include eliminating excess moisture, removing decaying wood, and regularly inspecting property for signs of infestation. Chemical treatments can also be used to protect property from termites.
Conclusion
Termites are amazing creatures that can do incredible things. They can build complex and intricate colonies, survive in extreme environments, and even help the environment through their decomposition of organic material. While they can cause damage to human structures, they can also be beneficial. It’s important to learn more about termites, both to be aware of the potential damage they can cause and to appreciate their unique abilities.