The mystery of how long flying termites live has intrigued scientists for years. This article seeks to uncover the answer to this question by examining and analysing the lifespans of different species of flying termites. By the end of this article, readers will have a better understanding of the lifespans of these creatures and be able to make informed decisions about how to deal with them.
Types of Termites

- Drywood Termites: They live in wood that is dry and not in contact with the soil.
- Subterranean Termites: These are the most destructive types of termites as they live and feed on wood and other materials that are in contact with the soil.
- Formosan Termites: They are aggressive and can cause widespread destruction, they live in colonies in soil or in moist timber.
- Conehead Termites: This type of termite is found in the Caribbean and southern Florida, they live in colonies and attack structural wood.
Flying Termites
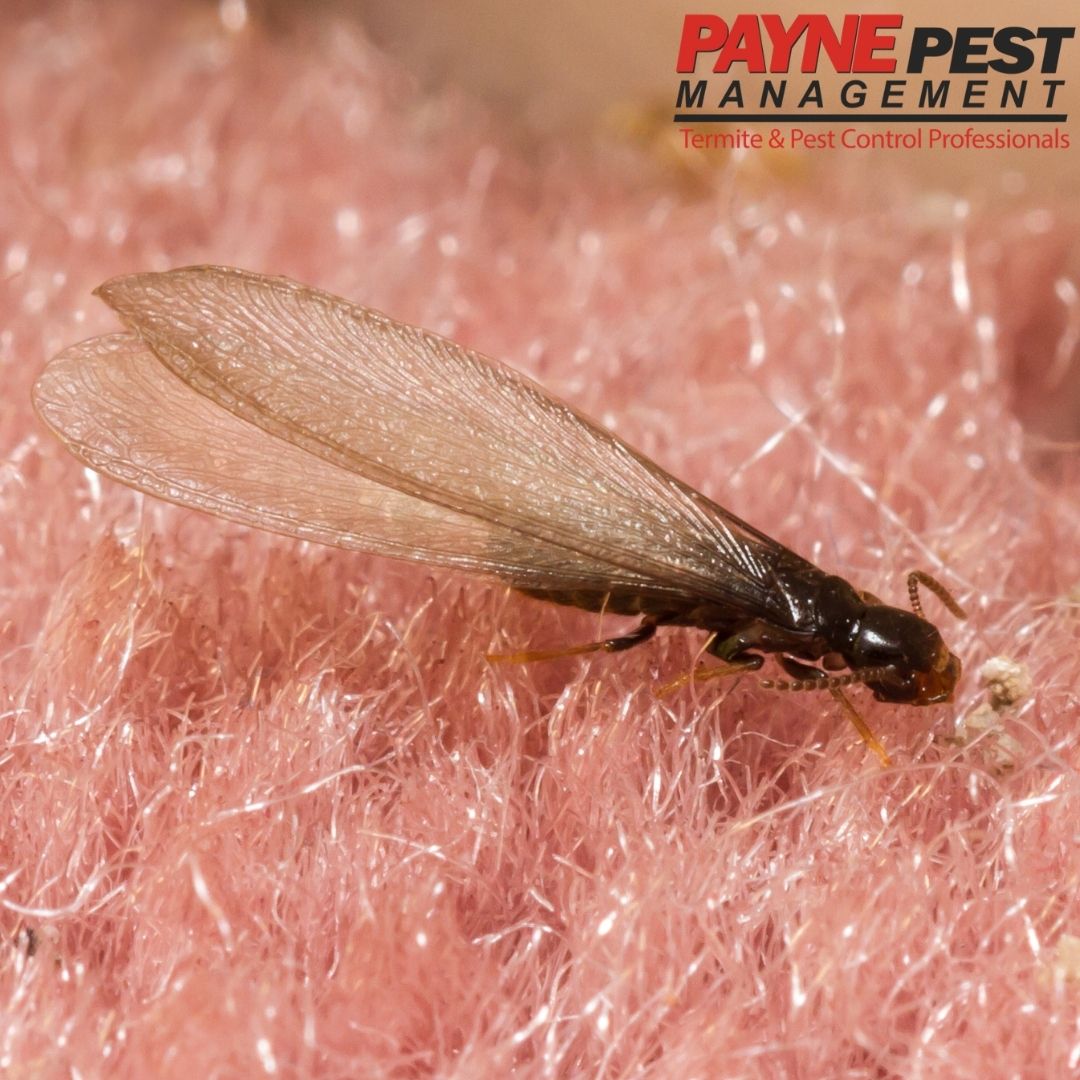

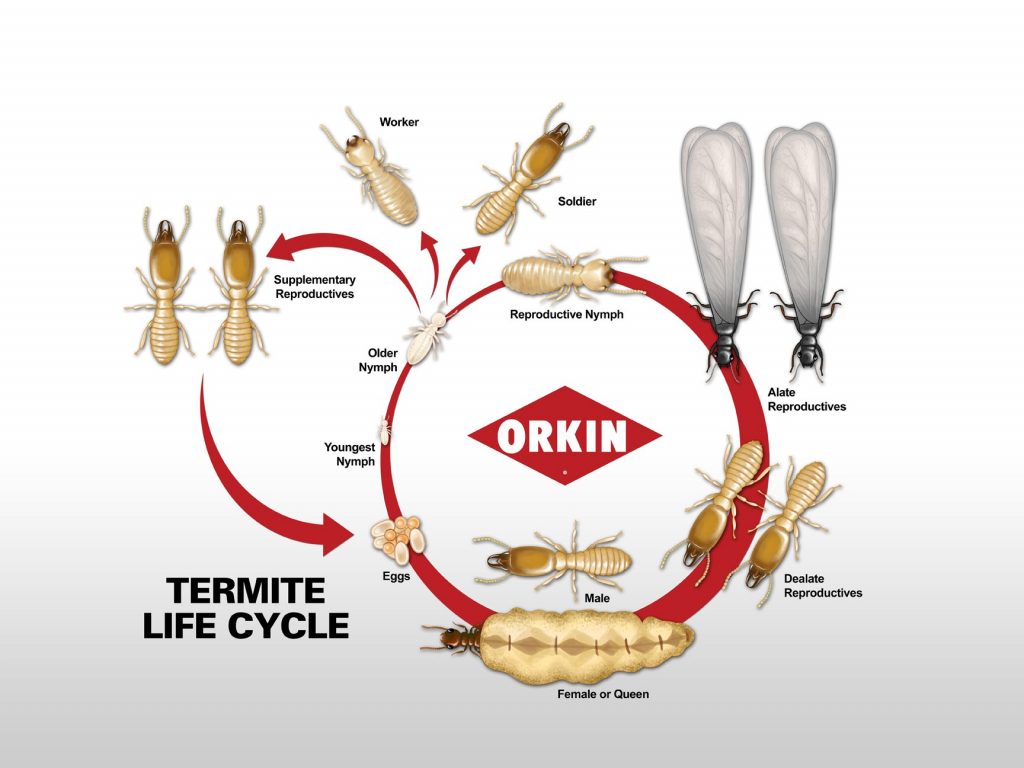
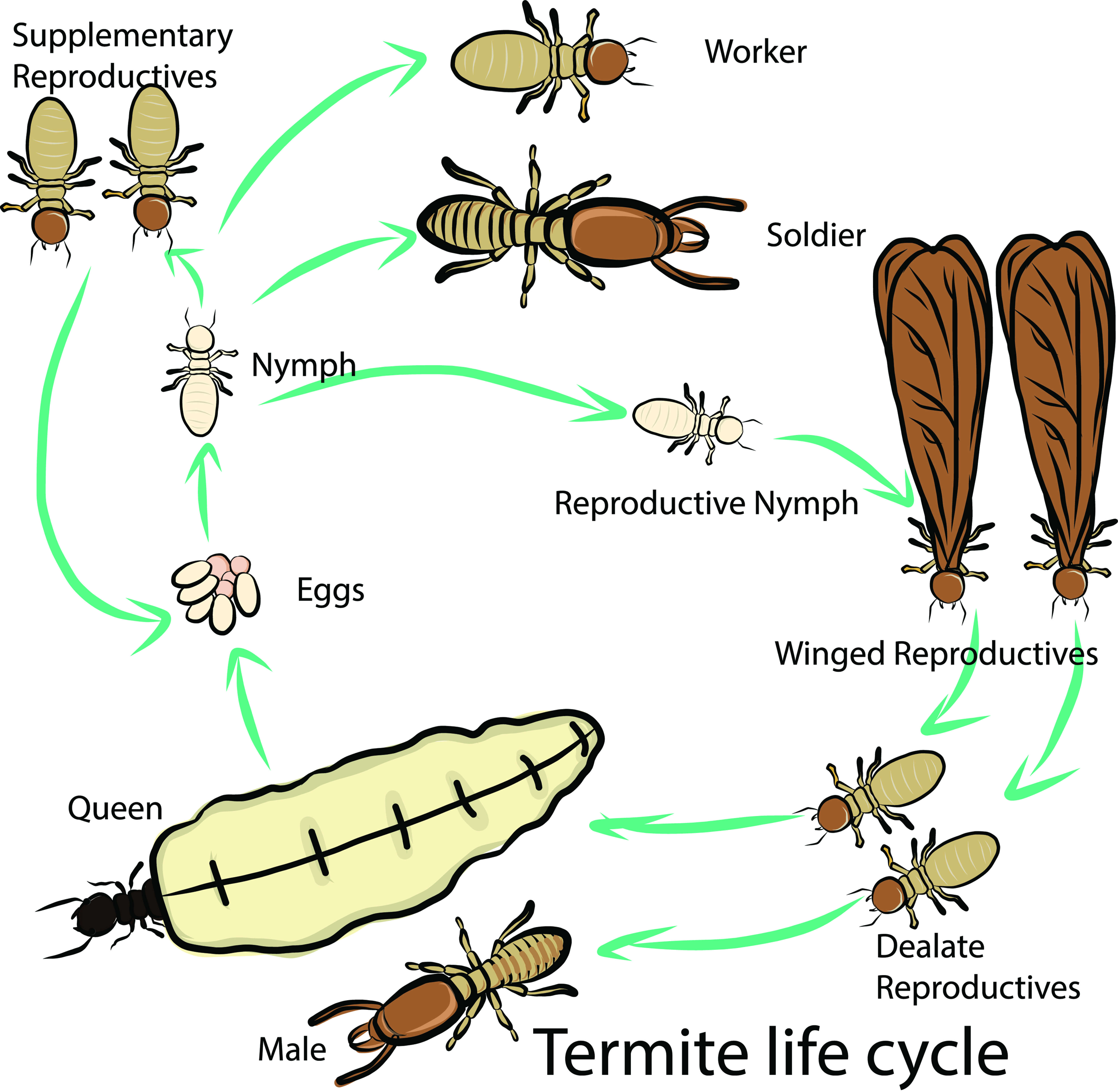
Flying termites, also known as alates, are the adults of the termite species that are able to fly. They are born from the mature termite colony, where they will live and develop for several weeks before emerging from the colony in large swarms. During this time, they will mate and form new colonies. Once this happens, the original colony will die off, since the alates are the only members of the species that are able to reproduce.
The lifespan of flying termites is relatively short and typically only lasts a few weeks. During this time, the alates will fly away from their colony in search of a mate, and they will die shortly afterwards, typically within a few days. It is also possible for them to be injured or killed by predators during their flight, further reducing their lifespan.
Lifespan of Flying Termites
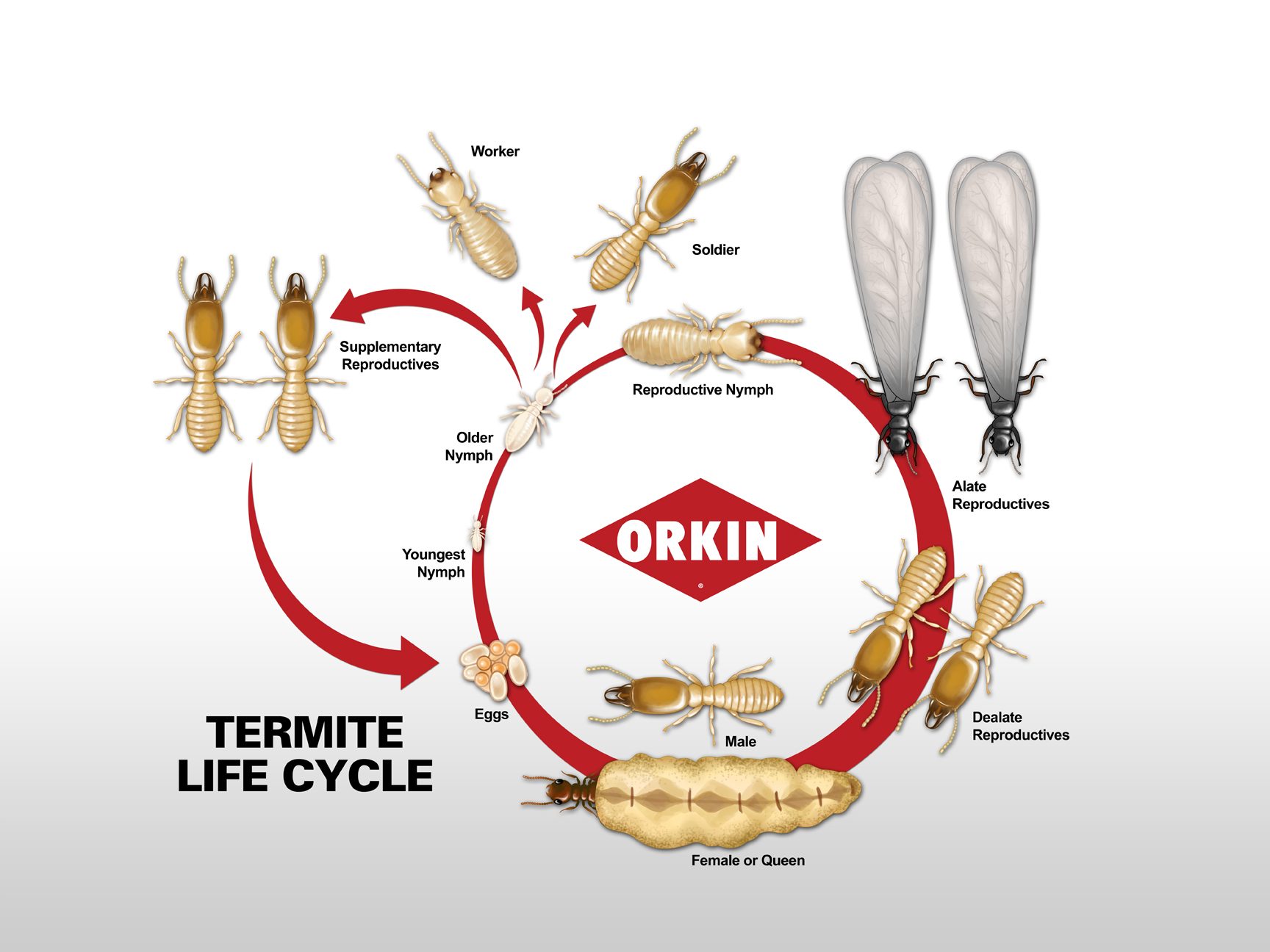
Flying termites, also known as alates, live an average lifespan of one to three months. During their short lifespan, they will fly, mate and then die shortly after. Flying termites are usually seen in the spring and summer, when temperatures are warm and the air is humid. After mating, the female termites will shed their wings and establish a new colony. The new colony will survive for many years as the female termite will lay thousands of eggs. The eggs will then hatch and produce a new generation of flying termites that will live and die in a similar manner.
Common Causes of Death
Flying termites typically have a lifespan of two to three months. During this time, the most common causes of death are starvation, predation, and natural disasters. Starvation can be caused by a lack of food sources, such as when the termite’s nest is destroyed or when they are unable to locate a suitable food source. Predation occurs when a predator, such as a bird or other insect, consumes the termite. Natural disasters, such as floods, storms, and droughts, can also kill flying termites.
Factors Influencing Lifespan
The lifespan of flying termites varies depending on a number of factors, such as the type of species, their environment, and the availability of food and water. The average lifespan of a flying termite is around six weeks, but this can vary depending on the conditions.
The type of species is a major factor in determining a flying termite’s lifespan. Some species live longer than others, while some are short-lived. The environment also plays a role, as termites need humidity and warmth to survive. The availability of food and water also affects their life expectancy; if food and water are scarce, the termite may not live as long.
The quality of the termite’s diet can also influence its life expectancy. Termites that feed on wood and other organic materials tend to live longer than those that feed on other insects or plants. Additionally, the presence of predators can reduce a termite’s lifespan, as they are constantly under threat of being eaten.
Lastly, the flying termite’s age can affect its life expectancy; older flying termites tend to have shorter lifespans than younger ones. As a result, flying termites that live in an environment that is conducive to their survival are more likely to live longer than those that do not.
How to Increase Flying Termites Lifespan
- Provide adequate nutrition by providing a balanced diet.
- Keep the environment clean, dry, and well-ventilated.
- Maintain the proper temperature and humidity levels.
- Keep the colony free of parasites and predators.
- Provide a safe nesting area.
- Provide adequate shelter from the elements.
- Keep the area free of toxic chemicals and pollutants.
- Reduce stress by providing regular periods of rest.
- Ensure the colonies have access to fresh air and plenty of water.
Pest Control Strategies
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Remove Sources of Moisture | Termites need a source of moisture to survive, so repair any water leaks, eliminate standing water, and install a dehumidifier to reduce moisture in the air. |
| Eliminate Access to Food Sources | Remove any wood, paper, and other materials that termites can feed on. Make sure to store firewood away from your home and keep mulch several feet away. |
| Seal Any Gaps or Cracks | Fill any cracks in walls and foundations with caulking or sealant. Make sure to check your door and window frames for any gaps or cracks. |
| Use Baits or Traps | Baits and traps can be used to help identify or eliminate a termite infestation. These options are available at most hardware stores. |
| Call a Professional | If you suspect a termite infestation, contact a pest control specialist for an inspection and to discuss treatment options. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Average Lifespan of a Flying Termite?
Flying termites typically live for an average of eight to ten weeks. During this time, they will mate and disperse the reproductive cells that will eventually produce the next generation of termites. After they have mated, they die shortly thereafter.
How does the lifespan of a flying termite compare to that of other termites?
Flying termites have a much shorter lifespan than their non-flying counterparts. The average lifespan of a flying termite is only about one to two months, while the lifespan of non-flying termites is usually between two and five years. In addition, flying termites do not form colonies or reproduce, which further limits their lifespan.
What Environmental Factors Impact the Lifespan of a Flying Termite?
Environmental factors significantly affect the lifespan of a flying termite. Temperature, humidity, air and food availability all play a role in determining how long a flying termite will live. Temperature extremes can cause a termite to enter a state of dormancy, reducing its lifespan. Humidity levels should be between 40-60% for optimal health, as too much or too little moisture can cause death. Air flow is also important, as termites require a certain amount of oxygen to survive. Finally, food availability is also a key factor, as termites need a steady supply of food to thrive.
Are there any known techniques to extend the life of a flying termite?
Providing the right environmental conditions is key to extending the life of a flying termite. The ideal environment should be moist, with temperatures between 20-30°C. It is also important to reduce stress levels by avoiding overcrowding and ensuring they have access to food and water. Additionally, proper hygiene and pest control around the home is essential to help keep flying termites away.
Are there any differences in the lifespan of male and female flying termites?
Research indicates that the lifespan of male flying termites is typically shorter than that of female flying termites. Male termites are typically seen only during mating season, when they fly out of their nests and search for female partners. During this time, they are exposed to a variety of environmental hazards and predators, meaning they do not live as long as female flying termites. Female flying termites, on the other hand, typically remain in the safety of the nest throughout their lifespans.
Conclusion
The lifespan of flying termites is largely determined by their environment and the availability of suitable resources. In general, flying termites can live for a few weeks to several months. In order to maximize their longevity, they need to find food and water sources, as well as suitable shelter. Additionally, flying termites may be able to live longer when they are able to find other flying termites to mate with. Ultimately, the life expectancy of flying termites will depend on the conditions of their environment.