Termites are small, destructive insects that can wreak havoc on homes and other structures. But how long do termites live? In this article, we will explore the lifespan of these destructive insects and the various factors that can influence their longevity.
Types of Termites
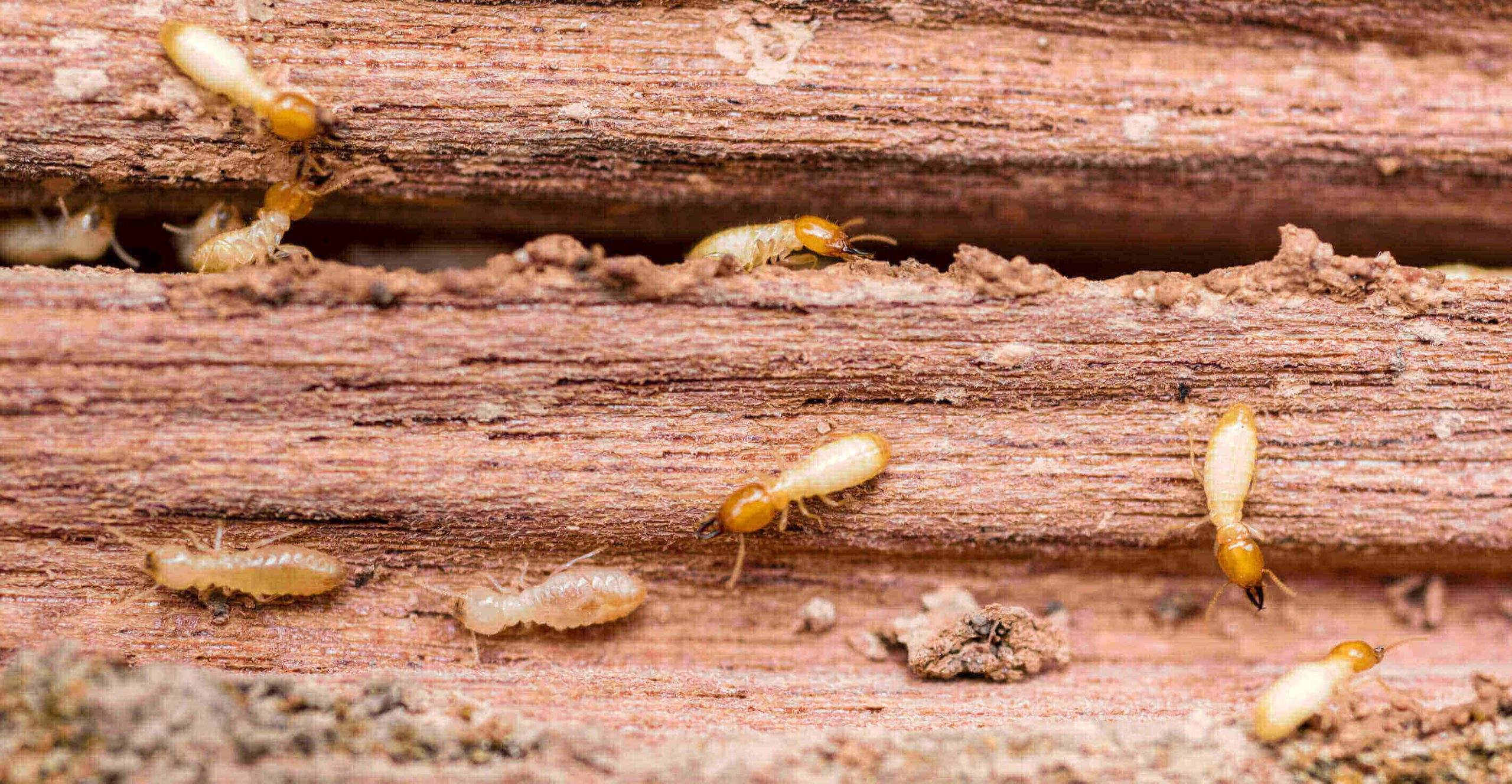

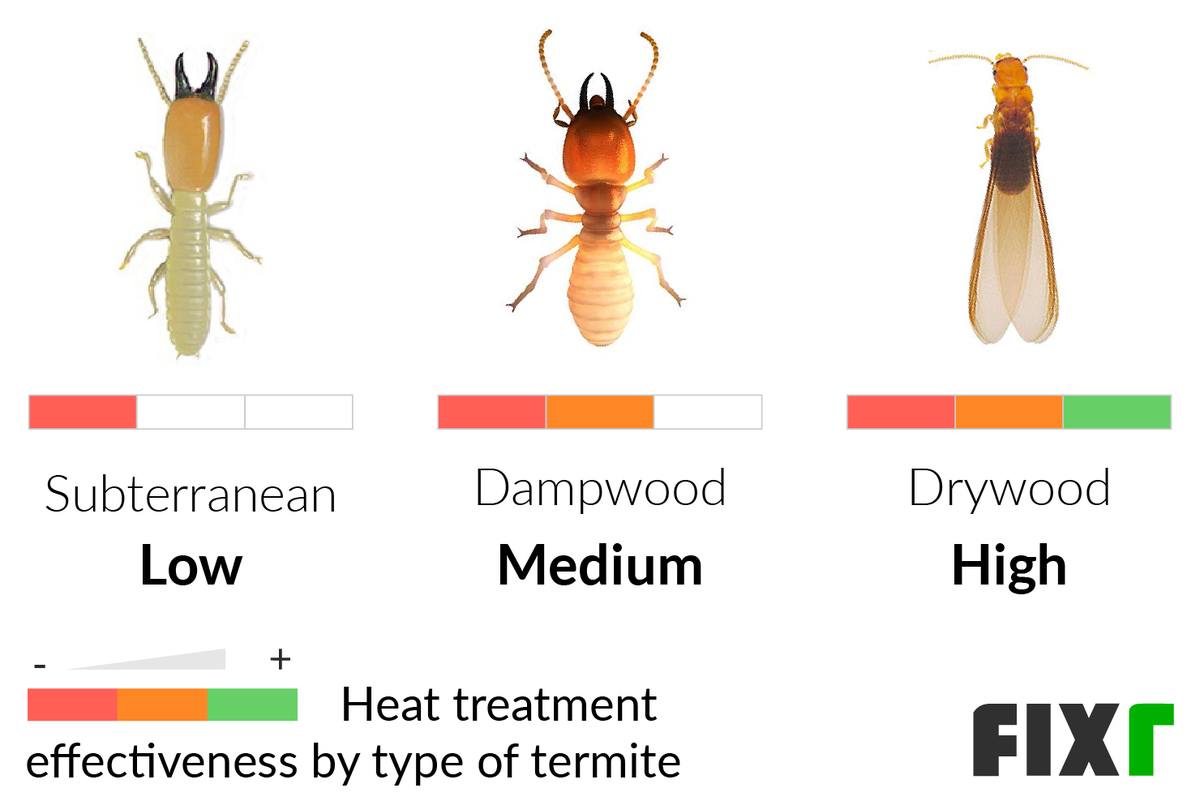
- Subterranean Termites
- Dampwood Termites
- Drywood Termites
- Formosan Termites
Subterranean termites live in the ground and build mud tunnels up the sides of buildings to access food sources. Dampwood termites are found in wood with high moisture content, such as rotting logs or stumps. Drywood termites live in dry wood and can infest furniture and other wooden structures. Formosan termites are a type of subterranean termite that are native to parts of Asia, but have spread to other parts of the world. These termites can cause more damage to buildings than other types of termites due to their large colonies.
Factors Affecting Lifespan of Termites
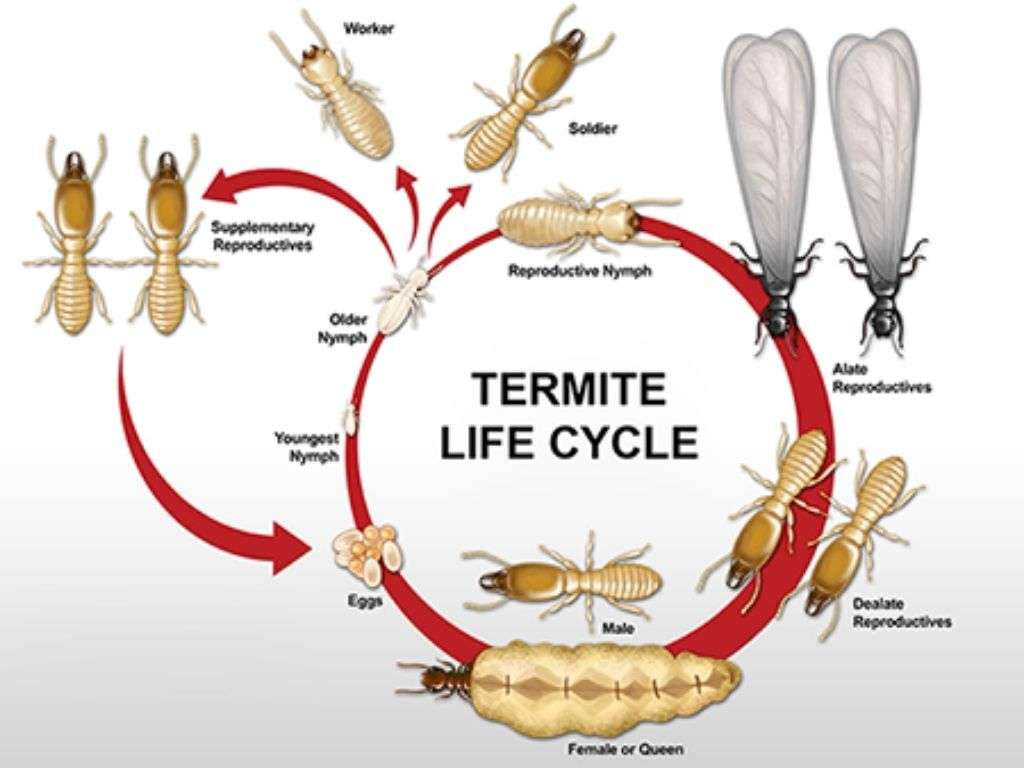
| Factor | Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Species | Termite species can live anywhere between 1-30 years. |
| Climate | Termites can live longer in warmer climates. |
| Nutrition | A well-fed termite colony can live over 25 years. |
| Predators | Predators, such as ants and spiders, can reduce termite lifespan. |
| Pathogens | Disease-causing pathogens, such as fungi and bacteria, can reduce lifespan. |
Different species of termites have differing lifespans, ranging from 1-30 years. In general, termites can live longer in warmer climates and with an adequate food supply. Predation by other insects and spiders can reduce their lifespan, as can pathogens such as fungi and bacteria. Overall, a well-fed termite colony can live over 25 years.
Nutrition
- Termites primarily feed on cellulose, a structural component of plants.
- Termites’ diet usually consists of wood, leaves, grasses, and soil.
- Termites are known to feed on other sources of nutrition such as fabrics, paper, and cardboard.
- Termites have an internal organ that produces cellulase, an enzyme that breaks down cellulose.
- Termites have a symbiotic relationship with protozoa that lives inside their digestive system, which produces additional enzymes that break down cellulose.
- Termites also obtain their nutrition from fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms.
- Termites also need to drink water to remain healthy.
Temperature

Temperature can have a strong effect on the lifespan of termites. Termites tend to survive longer in environments with a moderate temperature range between 70 to 90 degrees Fahrenheit. Extreme temperatures, such as those over 90 degrees Fahrenheit or below 50 degrees Fahrenheit, can cause termites to die quickly. Therefore, controlling the temperature of an environment can help to regulate termite populations.
Moisture

Termites require a moist environment to survive and thrive. They prefer high humidity, which can be found in dark, damp areas like basements, attics, and crawl spaces. As such, termites are typically found in areas where there is a lot of consistent moisture, such as near sources of water, like plumbing leaks and water-damaged wood.
Table:
| Moisture | Termite Life Expectancy |
| ——– | ———————- |
| High | Longer |
| Low | Short |
Competition

Termites are highly competitive species. They compete with each other for food and other resources. In order to survive, they must constantly compete for food, shelter, and nesting sites. To do this, they rely heavily on their social behavior, which includes cooperative behavior, communication, and aggressive competition.
In the wild, termites are often found competing for food with other insects and animals. They also compete for nesting sites, which provide safe places for them to live and breed. Termites also compete with other species for resources, such as wood and other cellulose-based materials.
| Competitors | Competition |
|---|---|
| Insects and other animals | Food |
| Other termites | Nesting sites |
| Other species | Wood and other cellulose-based materials |
Competition for resources is a major factor in the survival of termites, as it helps them to find food, shelter, and nesting sites that are suitable for their needs. Additionally, this competition helps to keep the population size in check, as the species that are better suited to the environment will out-compete weaker species.
Behavior of Termites
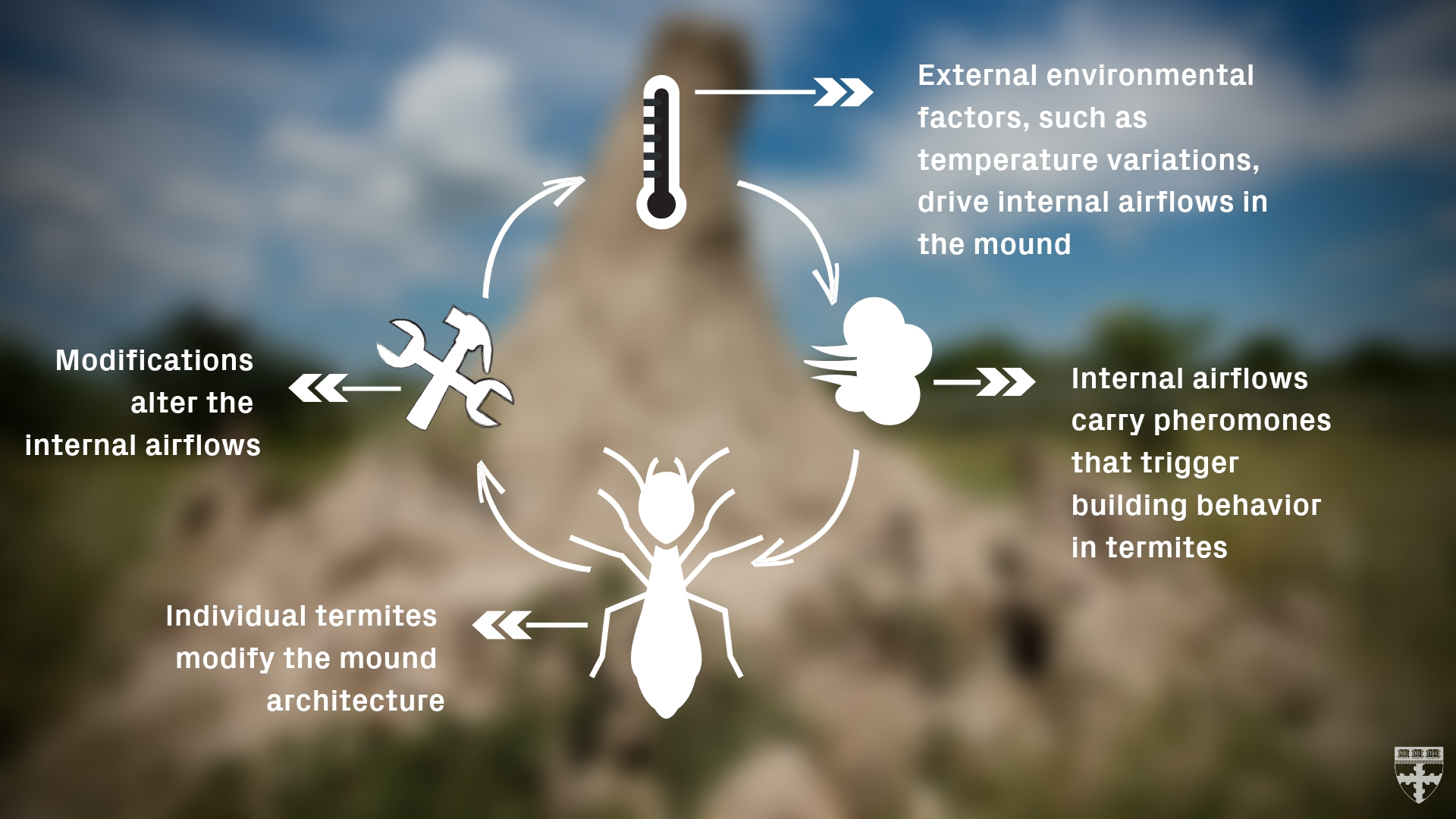
- Form complex social structures
- Live in colonies
- Communicate through chemical and physical signals
- Feed on wood, paper, and other materials containing cellulose
- Work together to build structures such as tunnels and galleries
- Divide tasks among castes such as soldiers, workers, and reproductives
- Work 24 hours a day
- Construct mud walls to protect their colonies
Nesting
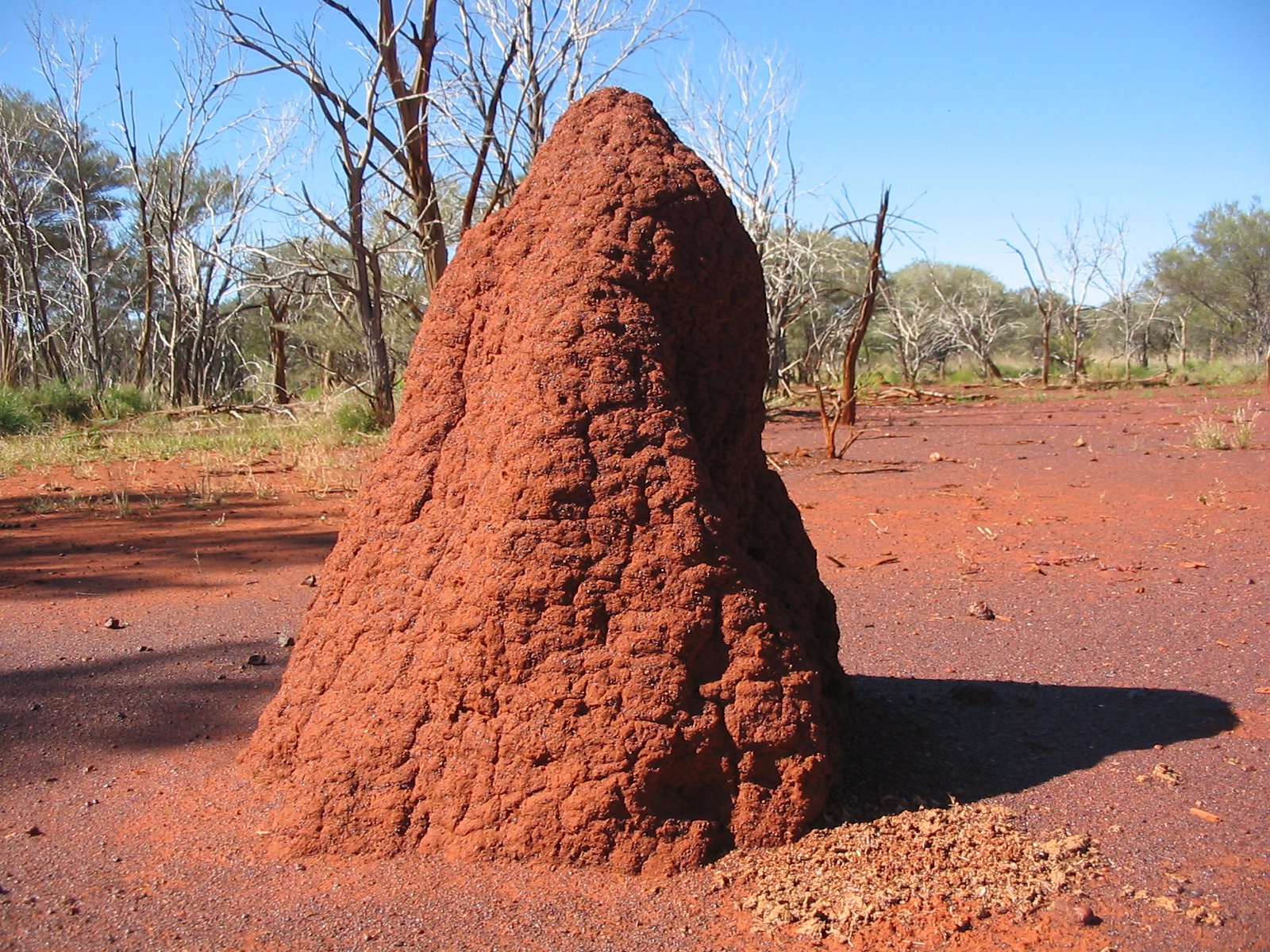

Termites build nests to provide shelter and protection for their colonies. They build nests using soil, wood, and feces. The nests usually have several chambers that are connected to each other by tunnels. The central chamber is the most important, since it serves as the shelter and breeding ground for the queen and her offspring. It is also where food is stored and the colony is able to survive during times of drought. The other chambers are used for egg-laying, nursing, and food storage. Nests can be found in the ground, in trees, in dead wood, and in buildings. Termites can live in their nests for up to 15 years, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Feeding
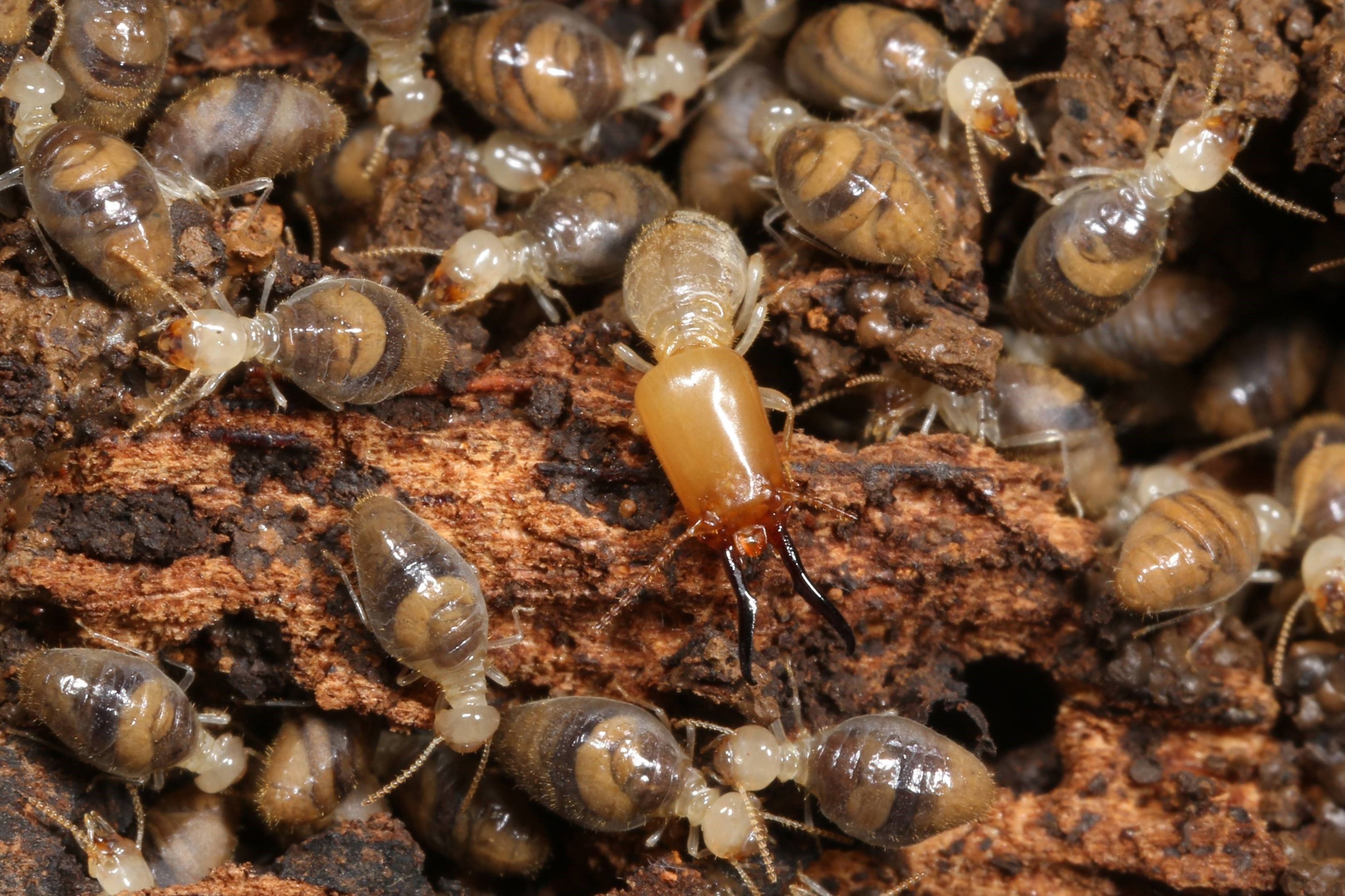

- Termites feed on wood, paper, insulation, and other materials containing cellulose.
- They feed on dead plants, trees, and wood that has already been damaged by fungi or other organisms.
- Termites feed on the wood of living plants, including trees, shrubs, and grasses.
- They feed on dead plant material, including decaying leaves, twigs, and bark.
- They also feed on other insects, including other termites.
Colony Growth
Termite colonies typically grow slowly at first; it may take several years for the colony to reach its full size. Once the colony is mature, it can contain millions of termites and span several acres of land. As the colony grows, the termites build elaborate, interconnected tunnels and chambers in the soil, creating a large, hidden network that is essential for their survival. These tunnels provide the termites with protection from predators and the elements, as well as access to food sources.
Average Lifespan of Termites
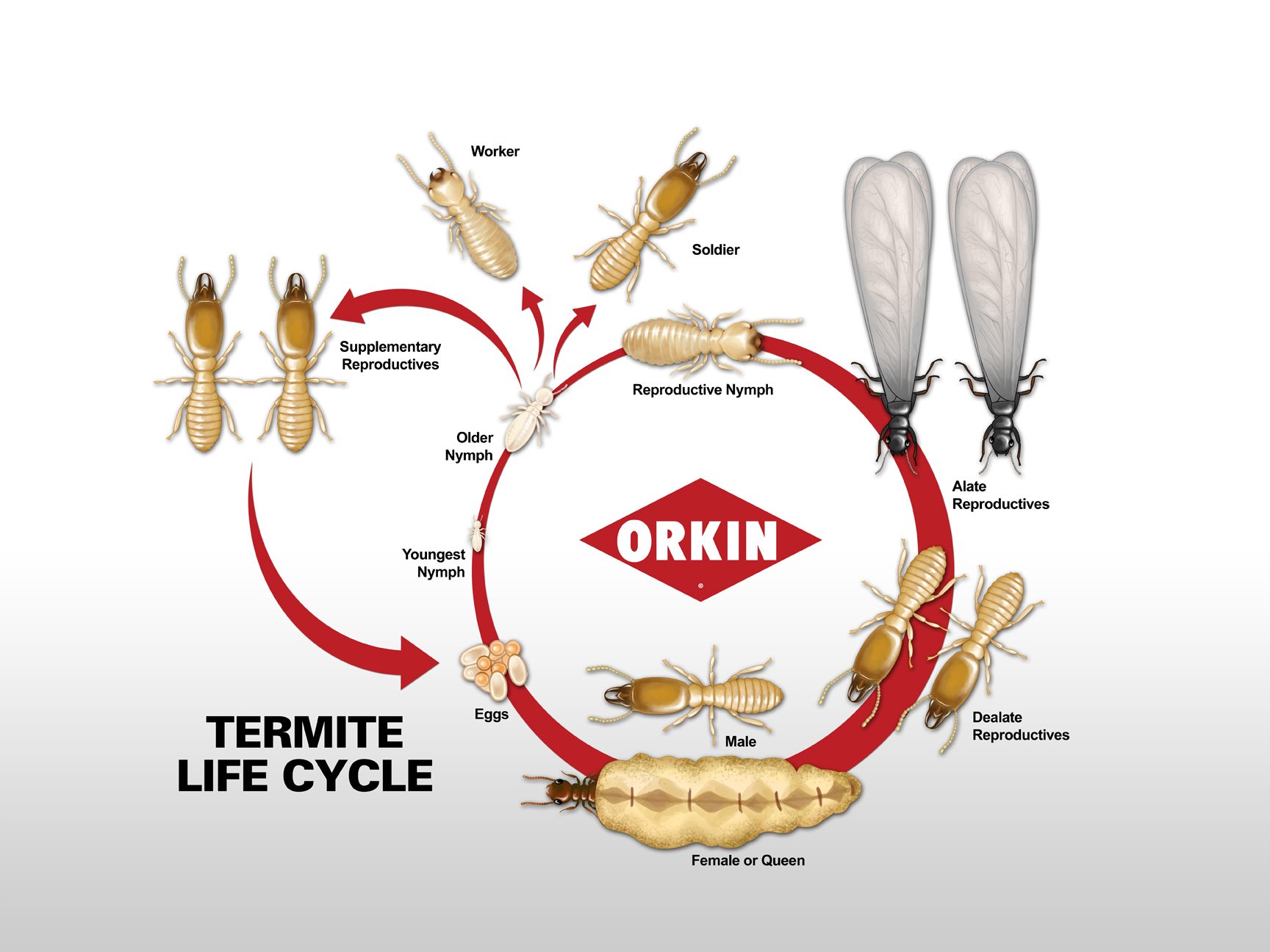
| Termite Type | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Subterranean Termite | 3-5 years |
| Drywood Termite | 2-3 years |
| Formosan Termite | 5-7 years |
The average lifespan of termites depends on the type of termite. Subterranean termites typically live for 3-5 years, while drywood termites generally survive for 2-3 years. Formosan termites usually live for 5-7 years.
Impact of Termites on Humans
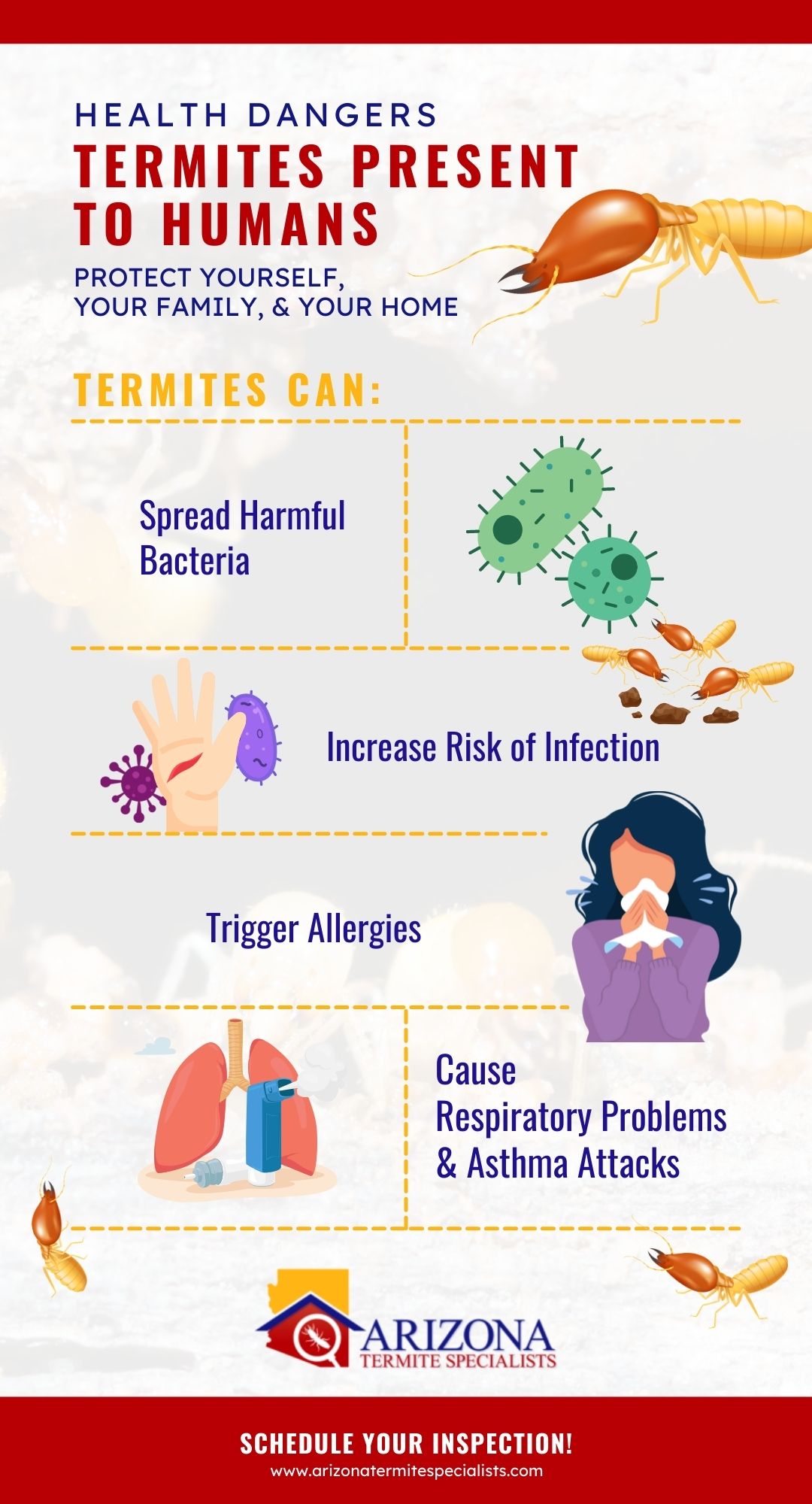
- Termites can cause serious damage to structures and furniture made from wood, paper, cloth, and other cellulose materials.
- They can destroy books, documents, wallpaper, carpets, insulation, and even swimming pool liners.
- Termites can also cause structural damage to buildings, resulting in costly repairs.
- They can contaminate food sources and cause respiratory problems in humans.
- Termites can also trigger allergies and asthma attacks in people who are sensitive to their presence.
Preventive Measures
| Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Inspection | Get an annual inspection of your home and surrounding area to check for signs of termites. |
| Eliminate Moisture | Make sure all moisture sources are eliminated or kept to a minimum, including leaky pipes, air conditioners, and downspouts. |
| Eliminate Wood/Paper | Remove all wood, paper, and debris from the area around your home. |
| Seal Cracks | Seal all cracks and crevices in your home’s foundation and walls to prevent termites from entering. |
| Eliminate Food Sources | Remove or properly store all food sources, such as pet food, wood piles, and compost piles. |
| Chemical Barriers | Treat your home with chemicals to create a barrier that termites cannot penetrate. |
Structural Protection
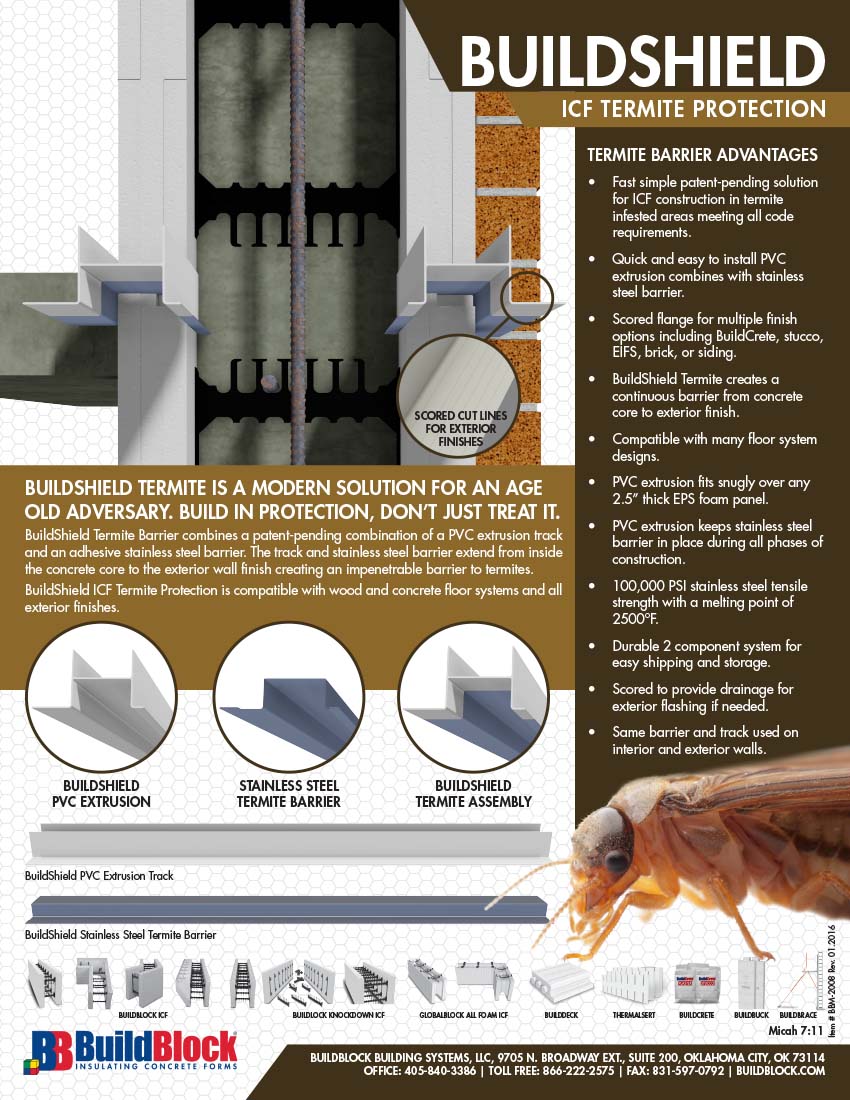
Termites can cause severe damage to a structure if left unchecked. To protect a structure from termites, homeowners can use a variety of methods. Barriers can be installed around the perimeter of the structure to keep termites from entering. There are also chemical treatments available that can be used to treat wood and soil to prevent termite infestations. Finally, preventing excessive moisture around the structure can also help keep termites from settling in.
Exclusion
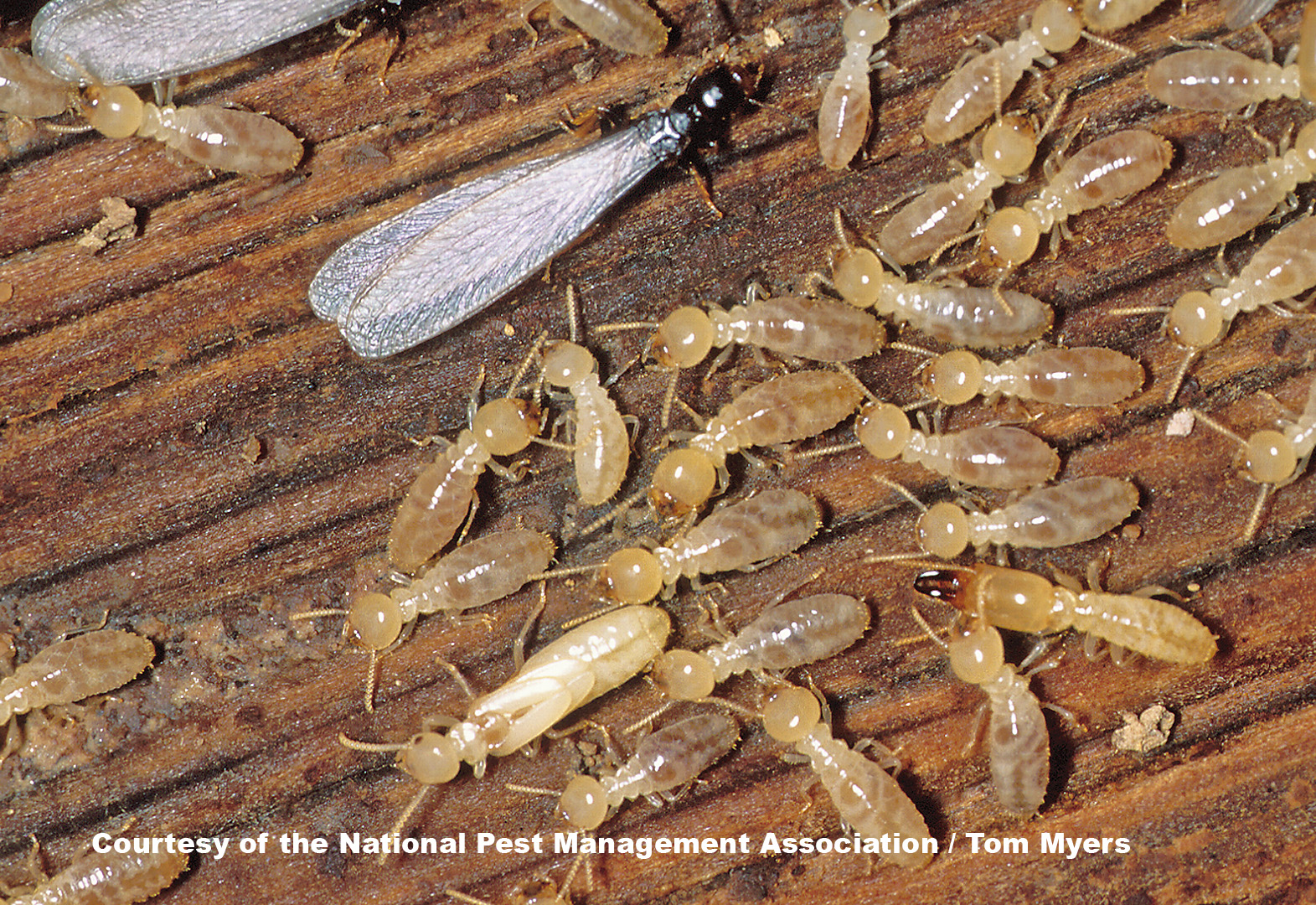

Termites typically live for up to five years, but this lifespan can be extended if exclusionary measures are taken. This includes sealing potential entry points, such as cracks in foundations, and keeping the home and yard free of wood, mulch, and other organic material.
| Measurement | Description |
|---|---|
| Sealing potential entry points | Fill cracks in foundations, repair window and door frames, and seal any other potential entry points. |
| Keeping the home and yard free of wood, mulch and other organic material | Remove stumps, logs, and other wood debris near the house, and keep mulch and other organic material away from the foundation. |
| Regular inspection | Schedule regular inspections of the home and yard to identify any potential entry points or areas of termite activity. |
Following these steps can help to significantly extend the lifespan of termites in a home.
Baiting
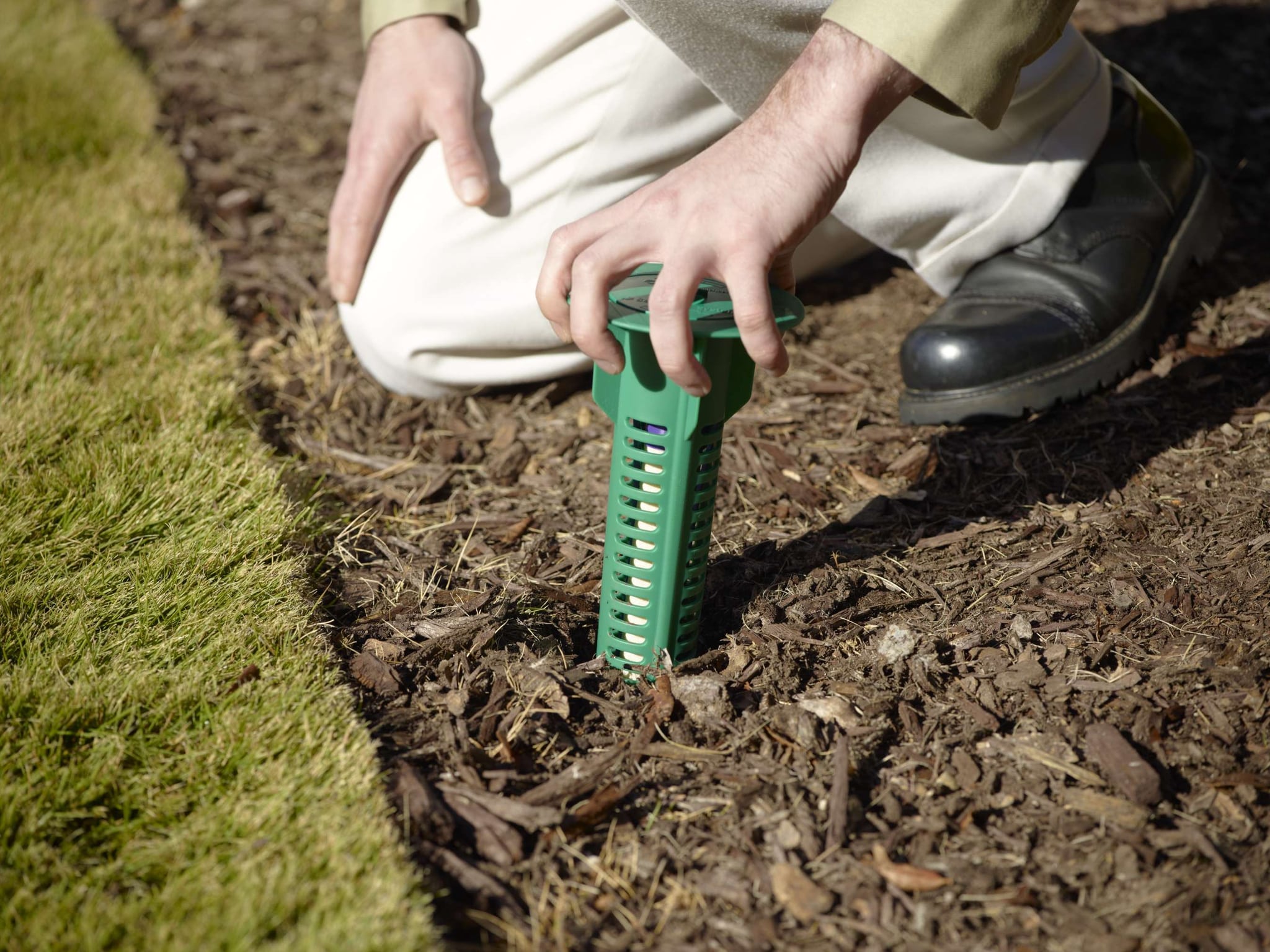

Baiting is an effective way to kill termites and can be done either above or below the ground. Baiting involves the placement of bait stations around the outside of a property, which contain a poisonous bait that is attractive to the termites. As the termites consume the bait, they become poisoned and die. Baiting is a slow process and can take up to several months to be effective, as the termites must take the bait back to the colony to be effective. Baiting is preferred over chemical treatments as it is non-toxic and does not require drilling.
Chemical Treatments
- Chemical treatments are one of the most common methods used to control termites.
- The chemicals used can be sprayed directly on the termites, or used in the form of baiting systems.
- These treatments usually have to be repeated on a regular basis to be effective.
- The duration of these treatments depends on the type of chemical used and the size of the infestation.
- Chemical treatments can be effective in eliminating termites, but they can also be dangerous if not handled properly.
Signs of Termites
Termites are difficult to detect since they are small and often remain hidden. But there are some telltale signs that they may be present in a structure.
| Sign | Description |
|---|---|
| Mud Tubes | Tunnels made of soil and saliva used to connect the nest to their food source. |
| Discarded Wings | Winged termites shed their wings after mating, leaving piles of wings near windowsills or other entry points. |
| Hollow Wood | Termites feed on wood, leaving behind hollowed or thinned boards and timbers. |
| Frass | Wood-colored droppings or pellets near wood structures can be a sign of an infestation. |
| Bubbling Paint | Bubbling paint or discoloration of wood can be a sign of moisture caused by an infestation. |
Treatment Options
There are several methods of controlling and eliminating termites, including chemical treatments, bait systems, and physical removal. Chemical treatments involve the application of termiticides to the soil around the building where termite infestation is found. Bait systems involve placing bait stations around the structure which attract termites, and contain insecticides to kill them. Physical removal involves the manual extraction of termite colonies and nests.
Frequently Asked Questions
What kind of damage can termites cause?
Termites cause extensive damage to wooden structures, including furniture, flooring, and walls. Termites may also damage non-wooden materials such as plaster, plastic, and drywall. In addition, they can cause damage to books, clothing, and other items made of fabric or paper. In extreme cases, termite damage can even compromise the structural integrity of a building.
How can homeowners identify a termite infestation?
Termites can be difficult to identify as they are small and often hidden. Signs of a termite infestation include wood that is hollowed or damaged, mud tubes on walls or foundation, small piles of wings near windows or doors, and visible swarms of termites. Homeowners may also notice small pinholes in wood and discarded wings near windowsills or door frames.
How can termite infestations be prevented?
Termite infestations can be prevented by eliminating any moisture around the home, keeping mulch and wood piles away from the foundation, sealing cracks in the foundation or walls, and repairing any water damage. Additionally, reducing the amount of wood-to-soil contact around the home is key. Finally, homeowners should ensure that gutters and downspouts are properly maintained and regularly inspect the home for signs of termite activity.
How Long is the Average Lifespan of a Termite?
The average lifespan of a termite is two to five years, depending on the species and the environment it lives in. Subterranean termites, for example, can live up to 10 years in the wild, while drywood termites typically live for five to seven years. Queen termites, on the other hand, can live up to 15 to 25 years.
Are there any natural remedies for controlling termite populations?
Yes, there are natural remedies for controlling termite populations. These include using nematodes, which are tiny worms, to attack termites; using orange oil, which is a natural insecticide; and using borax, which is a natural insecticide and repellent. Additionally, avoiding moisture buildup, keeping wood off the ground, and sealing cracks and crevices can help reduce the risk of termites entering your home.
Conclusion
Termite colonies live on average 10 years, though can survive up to 15 years or longer depending on the species, environmental conditions, and the availability of food. Although they are considered a pest because of their destructive nature, they are an important part of the ecosystem and play a vital role in decomposition and nutrient cycling. The lifespan of termites is relatively short, but their colonies can cause problems for homeowners for many years. To protect against termite damage, it is essential to be aware of the signs of an infestation and take the necessary steps to prevent and eliminate them.