Termites are one of the most interesting creatures in the animal kingdom. Not only do they have a complex relationship with the environment, but they also have a symbiotic relationship with wood. In this article, we will be exploring the unique symbiotic relationship between termites and wood, and how this relationship helps both creatures survive.
Types of Termites

Termites are social insects of the order Isoptera and the most abundant members of the suborder Nasutitermitina. They are divided into three main categories: dampwood, drywood, and subterranean.
Dampwood termites are found in humid and moist environments and are usually found in dead wood with high moisture content. They are usually visible to the eye as they don’t build mounds or tubes.
Drywood termites are found in dry and arid environments and feed on dry wood. They usually build mounds or tubes along the surface of wooden structures to provide them with protection from predators and the environment.
Subterranean termites are the most common and are found in most parts of the world. They feed on both dead and living wood, create underground tunnels and often build mud tubes to move around. They require moisture and high humidity levels to survive and can cause extensive damage to wooden structures if left untreated.
How Termites Eat Wood

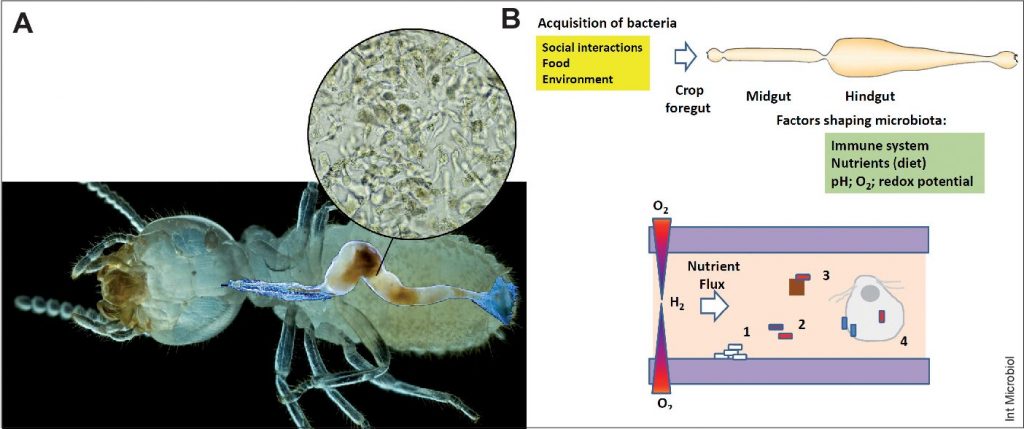
Termites are able to consume wood due to their symbiotic relationship with protozoa and bacteria in their digestive system. These microorganisms help break down the cellulose found in wood, which the termites can digest and use for energy. The protozoa and bacteria convert the cellulose into sugars and other nutrients, which are then absorbed by the termites. The termites also secrete special enzymes to aid in the breakdown of cellulose. The termites then regurgitate the wood to share with other members of the colony. This process occurs in the dark and damp chambers of the termite mound and is the primary source of food for the colony.
Symbiotic Relationship Between Termites and Protozoa
Termites and protozoa form a unique symbiotic relationship in the termite gut. Termites rely on the digestion of wood by protozoa in their gut to break down the cellulose in the wood into smaller molecules that can be used as energy sources. The protozoa in turn benefit from the warm and moist environment of the termite gut, as well as the nutrient-rich environment. In addition, the protozoa provide the termites with essential vitamins and amino acids that they are unable to synthesize themselves. This mutualistic relationship is essential for the survival of the termites and the protozoa. Without the protozoa, the termites would not be able to break down the cellulose in the wood and would not be able to survive.
Nutritional Benefits of the Relationship
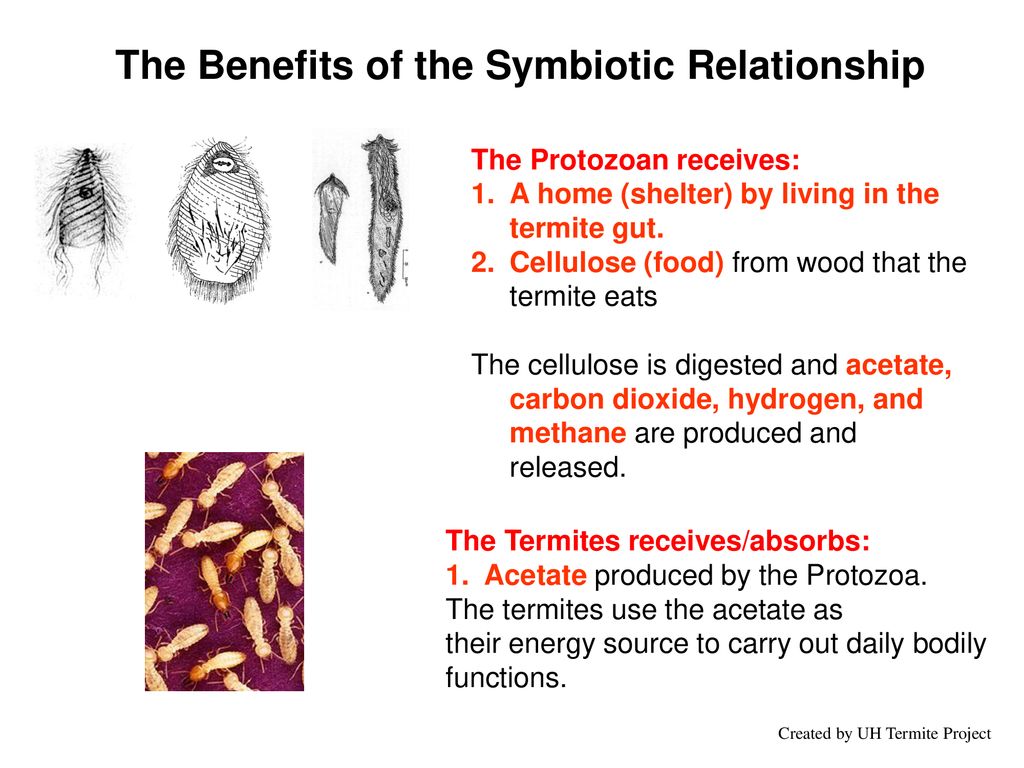
The symbiotic relationship between termites and the protists found in their gut allows them to digest wood and other cellulose materials that would otherwise be inaccessible to them. The protists break down the cellulose and release sugars, amino acids, and other nutrients, which the termites can then absorb and use for their own growth and development. This mutually beneficial relationship provides the termites with an easily accessible source of nutrition, while the protists receive protection and a place to live.
Significance of the Relationship
| Organism | Significance |
|---|---|
| Termites | Termites gain nutrition from wood, which helps them to survive in their environment. |
| Wood | Wood gets rid of cellulose and other materials that are not useful to plants, which helps protect the plants from damage. It also helps to maintain the balance of the ecosystem. |
The symbiotic relationship between termites and wood is significant in a number of ways. It provides termites with a steady food source, while also providing wood with nutrients, helping it to stay healthy. The relationship also helps to maintain the balance of the ecosystem, as termites break down wood and other materials that are not useful to plants. This helps protect plants from damage, and also helps to recycle nutrients back into the environment.
Negative Effects of the Relationship
| Organism | Negative Effects |
|---|---|
| Termites | Termites can cause extensive structural damage to buildings and other wooden structures, such as furniture. |
| Wood | Wood is weakened and weakened further if it is not repaired or replaced, leading to more damage and the need for costly repairs. |
Controlling Termites
- Inspect your property regularly for signs of termites.
- Remove any sources of moisture from your property as this attracts termites.
- Eliminate wood-to-soil contact in your property.
- Repair any leaks or other sources of moisture.
- Ventilate your property to reduce humidity levels.
- Remove any dead wood from your property.
- Seal any cracks or other entry points to your property.
- Treat your property with a pesticide or other insecticide.
- Install a termite barrier around your property.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Symbiotic Relationship between Termites and Wood?
Termites and wood have a symbiotic relationship, in which both species benefit from each other. Termites feed on wood, and in return, they help break down decaying wood, which helps enrich the soil with minerals and nutrients. This symbiotic relationship also helps keep forests healthy, as termites continually renew the soil, helping the trees to grow. In addition, termites provide food for other animals, such as birds, who feed on the termites.
How do protozoa help termites with the digestion of wood?
Protozoa found in the gut of termites play an important role in the digestion of wood. These protozoa possess enzymes that break down cellulose, the main component of wood, into smaller molecules. These molecules are then absorbed by the termites, allowing them to gain the necessary nutrients from the wood. The protozoa also produce a variety of other enzymes and acids which help to break down other components of wood, such as lignin, that would otherwise be indigestible. This symbiotic relationship between protozoa and termites allows them to thrive in their environment and survive on wood as their main food source.
What is the significance of the symbiotic relationship between protozoa and termites?
Termites and protozoa have a mutually beneficial relationship, whereby protozoa living in the gut of termites help them digest wood and in return, the termites provide the protozoa with food and shelter. This symbiotic relationship allows termites to consume wood, which is their main source of nutrition. The protozoa produce enzymes that help break down the cellulose present in wood and make it digestible to the termites. In return, the protozoa receive a steady supply of nutrition from the termites. The symbiotic relationship between protozoa and termites is essential for the survival of both species.
How does the mutualistic relationship between protozoa and termites aid in the consumption of wood?
Termites and protozoa have a mutualistic relationship in which protozoa break down lignocellulose in wood, which termites cannot break down on their own. The protozoa, which live in the termite’s gut, produce enzymes which break down the cellulose and lignin in the wood, making it easier for the termite to digest and access the nutrients. This relationship is beneficial to both organisms, as the protozoa receive a steady supply of food, and the termites can consume wood more efficiently.
How does the symbiotic relationship between termites and protozoa help the environment?
The symbiotic relationship between termites and protozoa is mutually beneficial, with the protozoa breaking down woody plant material that the termites can then digest. This process helps the environment by returning nutrients to the soil, which can then be used by other organisms. As a result, the symbiotic relationship between termites and protozoa helps to cycle nutrients, improve soil fertility and support the growth of other plants in the environment.
Conclusion
Termites and wood are a classic example of symbiotic relationships. Termites consume wood as their main energy source and in return, they help to break down the wood and return it to the soil as a source of nutrients. Termites also play an important role in the transfer of energy in the ecosystem by transferring energy from the wood to other organisms. This relationship is mutually beneficial and highlights the importance of maintaining natural ecosystems.